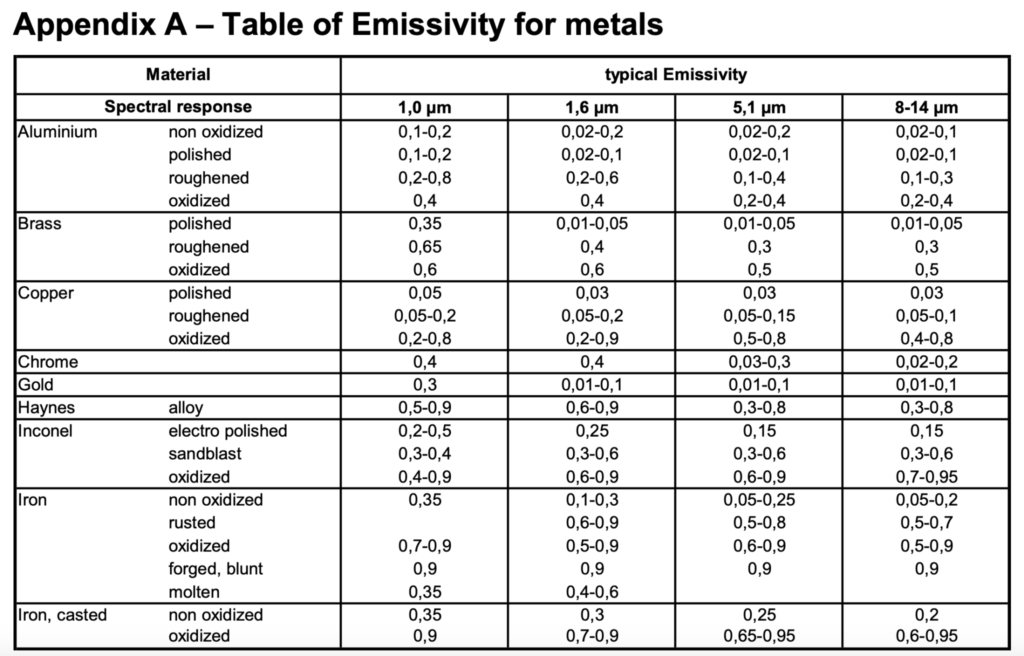
Emissivity Chart
Emissivity Chart - Thus, emissivity always falls between 0 and 1. Emissivity is essentially the ratio of the emissive power of a real body, compared to that of a blackbody. Emissivity of a body at a given temperature is the ratio of the total emissive power of a body to the total emissive power of a perfectly black body at that temperature. Emissivity ( ϵ ϵ ) is the ratio of radiation emitted by a surface to that emitted by a blackbody at the same temperature. The radiation heat transfer emissivity coefficients for some common materials like aluminum, brass, glass and many more. The emissivity (ε) of a material is the relative ability of its surface to emit heat by radiation. Watts of energy per unit of area. One of the ways to describe the infrared energy emitted by molecules is in terms of radiance: Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from a material's surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter, known as a blackbody, at the same temperature and wavelength and. As a blackbody emits the maximum amount of radiation possible over all. Emissivity can have a value from 0 (shiny mirror) to 1.0. Emissivity is the measure of an object's ability to emit infrared energy. Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from a material's surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter, known as a blackbody, at the same temperature and wavelength and. The emissivity, ε, of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in emitting energy as thermal radiation and varies between 0.0 and 1.0. By definition, a blackbody in thermal. Emissivity is essentially the ratio of the emissive power of a real body, compared to that of a blackbody. The ratio of the radiant energy emitted by a surface to that emitted by a blackbody at the same. The meaning of emissivity is the relative power of a surface to emit heat by radiation : Emissivity of a body at a given temperature is the ratio of the total emissive power of a body to the total emissive power of a perfectly black body at that temperature. Thus, emissivity always falls between 0 and 1. The emissivity (ε) of a material is the relative ability of its surface to emit heat by radiation. Watts of energy per unit of area. Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from a material's surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter, known as a blackbody, at the same temperature and wavelength and. The meaning of. By definition, a blackbody in thermal. Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from a material's surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter, known as a blackbody, at the same temperature and wavelength and. Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from an object's surface to the energy. The emissivity, ε, of the. Watts of energy per unit of area. Emissivity can have a value from 0 (shiny mirror) to 1.0. As a blackbody emits the maximum amount of radiation possible over all. The radiation heat transfer emissivity coefficients for some common materials like aluminum, brass, glass and many more. By definition, a blackbody in thermal. Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from a material's surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter, known as a blackbody, at the same temperature and wavelength and. Emissivity can have a value from 0 (shiny mirror) to 1.0. One of the ways to describe the infrared energy emitted by molecules is in terms of radiance:. Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from an object's surface to the energy. The ratio of the radiant energy emitted by a surface to that emitted by a blackbody at the same. The emissivity (ε) of a material is the relative ability of its surface to emit heat by radiation. Watts of energy per unit of. Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from a material's surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter, known as a blackbody, at the same temperature and wavelength and. Emissivity ( ϵ ϵ ) is the ratio of radiation emitted by a surface to that emitted by a blackbody at the same temperature. The emissivity (ε) of. Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from a material's surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter, known as a blackbody, at the same temperature and wavelength and. The meaning of emissivity is the relative power of a surface to emit heat by radiation : Emissivity ( ϵ ϵ ) is the ratio of radiation emitted. As a blackbody emits the maximum amount of radiation possible over all. Emissivity is the measure of an object's ability to emit infrared energy. The meaning of emissivity is the relative power of a surface to emit heat by radiation : The emissivity (ε) of a material is the relative ability of its surface to emit heat by radiation. By. As a blackbody emits the maximum amount of radiation possible over all. Emissivity can have a value from 0 (shiny mirror) to 1.0. The emissivity (ε) of a material is the relative ability of its surface to emit heat by radiation. Emissivity ( ϵ ϵ ) is the ratio of radiation emitted by a surface to that emitted by a. Emissivity of a body at a given temperature is the ratio of the total emissive power of a body to the total emissive power of a perfectly black body at that temperature. Thus, emissivity always falls between 0 and 1. As a blackbody emits the maximum amount of radiation possible over all. By definition, a blackbody in thermal. Emitted energy. By definition, a blackbody in thermal. The meaning of emissivity is the relative power of a surface to emit heat by radiation : One of the ways to describe the infrared energy emitted by molecules is in terms of radiance: Emissivity can have a value from 0 (shiny mirror) to 1.0. Watts of energy per unit of area. Emissivity of a body at a given temperature is the ratio of the total emissive power of a body to the total emissive power of a perfectly black body at that temperature. Emissivity ( ϵ ϵ ) is the ratio of radiation emitted by a surface to that emitted by a blackbody at the same temperature. The emissivity, ε, of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in emitting energy as thermal radiation and varies between 0.0 and 1.0. The radiation heat transfer emissivity coefficients for some common materials like aluminum, brass, glass and many more. Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from a material's surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter, known as a blackbody, at the same temperature and wavelength and. Emissivity is the measure of an object's ability to emit infrared energy. Emitted energy indicates the temperature of the object. As a blackbody emits the maximum amount of radiation possible over all. The ratio of the radiant energy emitted by a surface to that emitted by a blackbody at the same.Metals Surface emissivity. Download Table
What is Emissivity Infrared Pedak Meettechniek
Various Emissivity Coefficients Download Table
Emmissivity of Various Materials Infrared Training Institute
Ir Thermometer Emissivity Chart
Emissivity Table PDF
Emissivity values for several materials Download Scientific Diagram
Selecting HiE or LoE based on emissivity table
Emmissivity of Various Materials Infrared Training Institute
Table of Total Emissivity
Emissivity Is Defined As The Ratio Of The Energy Radiated From An Object's Surface To The Energy.
The Emissivity (Ε) Of A Material Is The Relative Ability Of Its Surface To Emit Heat By Radiation.
Thus, Emissivity Always Falls Between 0 And 1.
Emissivity Is Essentially The Ratio Of The Emissive Power Of A Real Body, Compared To That Of A Blackbody.
Related Post: