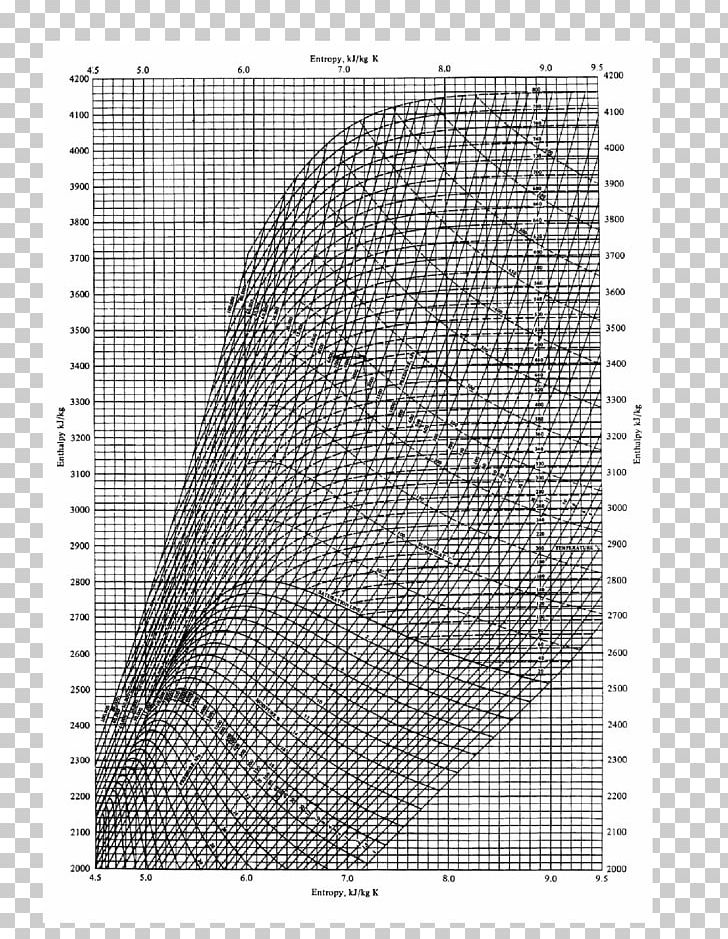
Entropy Chart
Entropy Chart - It is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that. Entropy is defined as a measure of a system’s disorder or the energy unavailable to do work. It is a concept that permeates every facet of reality, shaping the flow of time, the behavior of systems, and even. It is an extensive property of a thermodynamic system, meaning its value changes depending on the amount of matter. The meaning of entropy is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that is also usually considered to be a measure of the system's. Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The second law of thermodynamics states that the total entropy of a system either increases or remains constant in any spontaneous process; Entropy is not just an abstract principle tucked away in physics textbooks. The second law of thermodynamics is best expressed in terms of a change in the thermodynamic variable known as entropy, which is represented by the symbol s. Entropy, the measure of a system’s thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work. The second law of thermodynamics is best expressed in terms of a change in the thermodynamic variable known as entropy, which is represented by the symbol s. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical. It is a concept that permeates every facet of reality, shaping the flow of time, the behavior of systems, and even. The second law of thermodynamics states that the total entropy of a system either increases or remains constant in any spontaneous process; Entropy is not just an abstract principle tucked away in physics textbooks. Entropy is the measure of the disorder of a system. The meaning of entropy is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that is also usually considered to be a measure of the system's. Entropy, the measure of a system’s thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work. Entropy is a scientific concept commonly associated with disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. It is an extensive property of a thermodynamic system, meaning its value changes depending on the amount of matter. Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. Entropy is a key concept in physics and chemistry, with application in other. Entropy is the measure of the disorder of a system. It is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that. Entropy is defined as a measure of a. The second law of thermodynamics states that the total entropy of a system either increases or remains constant in any spontaneous process; Entropy is not just an abstract principle tucked away in physics textbooks. It is a concept that permeates every facet of reality, shaping the flow of time, the behavior of systems, and even. Entropy is the disorder of. Entropy, the measure of a system’s thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work. Entropy is not just an abstract principle tucked away in physics textbooks. Entropy is the measure of the disorder of a system. Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The second law of thermodynamics. It is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that. The second law of thermodynamics is best expressed in terms of a change in the thermodynamic variable known as entropy, which is represented by the symbol s. Entropy is the disorder of a system, but that means a lot more than making a mess of a. It is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that. The meaning of entropy is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that is also usually considered to be a measure of the system's. It is an extensive property of a thermodynamic system, meaning its value changes depending on the amount of. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical. Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. Because work is obtained from ordered molecular motion,. It is an extensive property of a thermodynamic system, meaning its value changes depending on the amount of matter. Entropy is the disorder of a. Entropy is a key concept in physics and chemistry, with application in other. Entropy is a scientific concept commonly associated with disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. It is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that. The meaning of entropy is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that is also usually considered. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical. The second law of thermodynamics states that the total entropy of a system either increases or remains constant in any spontaneous process; Entropy is a scientific concept commonly associated with disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. Entropy is the measure of the disorder of a system. It is a concept. Entropy is defined as a measure of a system’s disorder or the energy unavailable to do work. Entropy is the disorder of a system, but that means a lot more than making a mess of a room. Because work is obtained from ordered molecular motion,. Entropy, the measure of a system’s thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for. Entropy, the measure of a system’s thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work. Entropy is a scientific concept commonly associated with disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. Entropy is a key concept in physics and chemistry, with application in other. It is an extensive property of a thermodynamic system, meaning its value changes depending on the amount. The second law of thermodynamics is best expressed in terms of a change in the thermodynamic variable known as entropy, which is represented by the symbol s. Entropy is a key concept in physics and chemistry, with application in other. It is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that. Entropy is a scientific concept commonly associated with disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. Entropy, the measure of a system’s thermal energy per unit temperature that is unavailable for doing useful work. The meaning of entropy is a measure of the unavailable energy in a closed thermodynamic system that is also usually considered to be a measure of the system's. Entropy is not just an abstract principle tucked away in physics textbooks. Entropy is defined as a measure of a system’s disorder or the energy unavailable to do work. It is an extensive property of a thermodynamic system, meaning its value changes depending on the amount of matter. It is a concept that permeates every facet of reality, shaping the flow of time, the behavior of systems, and even. Because work is obtained from ordered molecular motion,. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical.Enthalpyentropy Chart Diagram Thermodynamics Water PNG, Clipart, Angle, Area, Artwork
Explain Water Temperature Enthalpy Diagram For Water Methane
Entropy Table
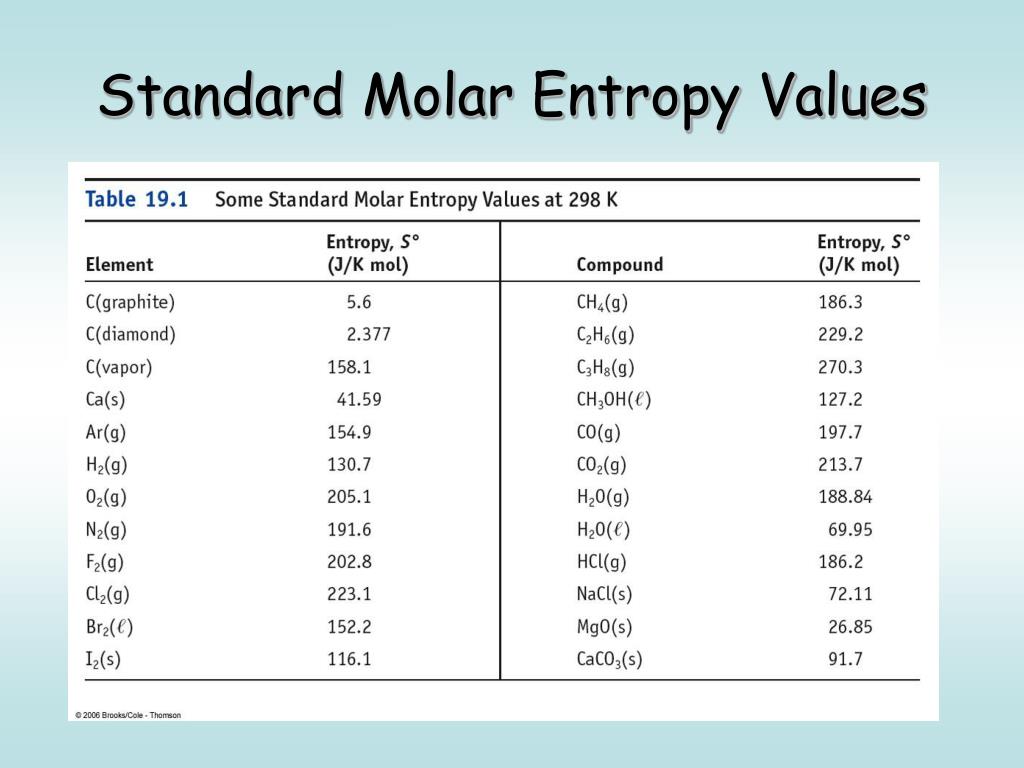
PPT Chapter 19 Principles of Reactivity Entropy and Free Energy PowerPoint Presentation
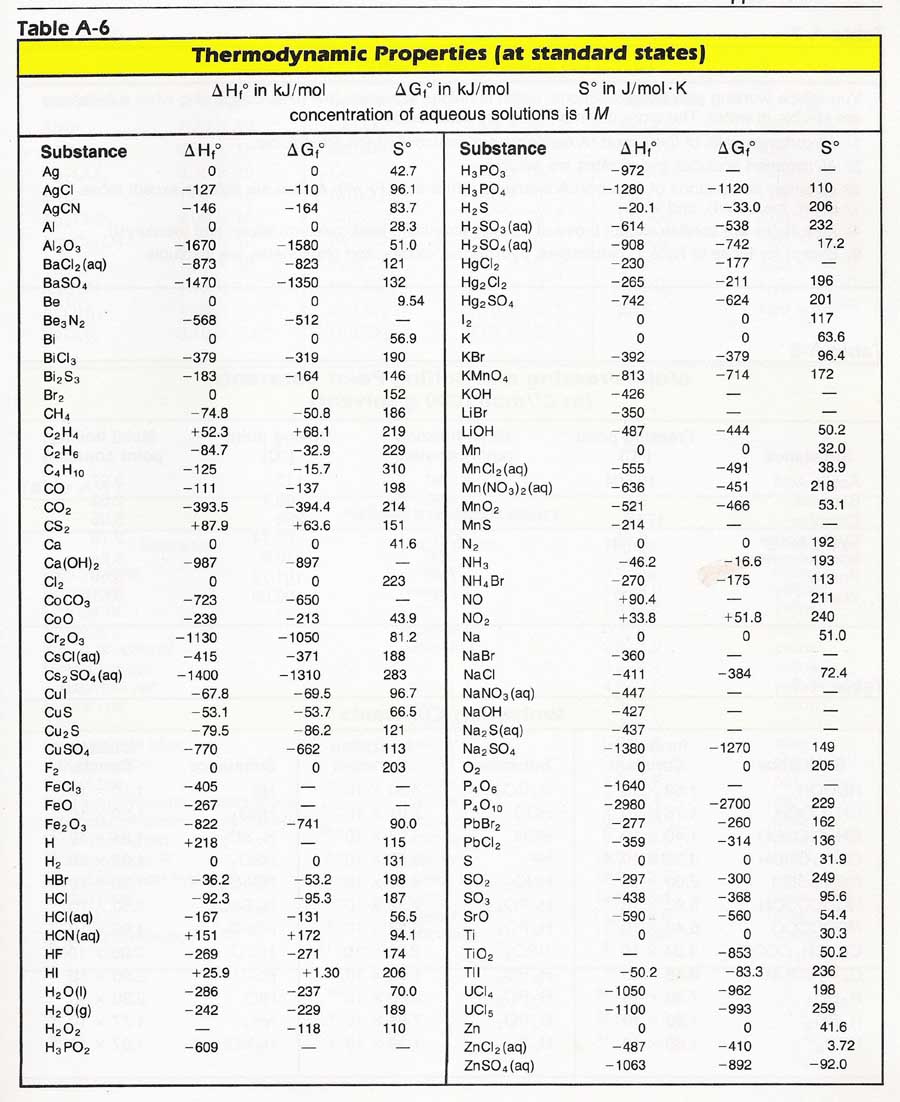
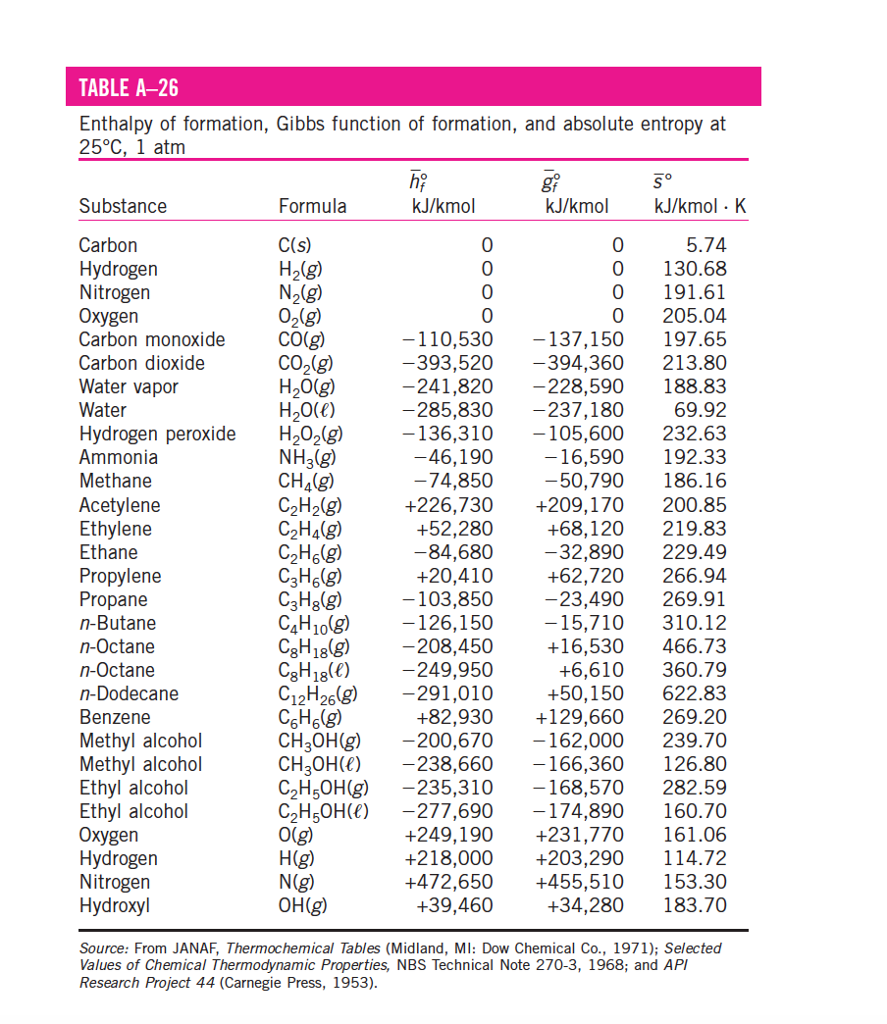
TABLE A286 Enthalpy of formation, Gibbs function of
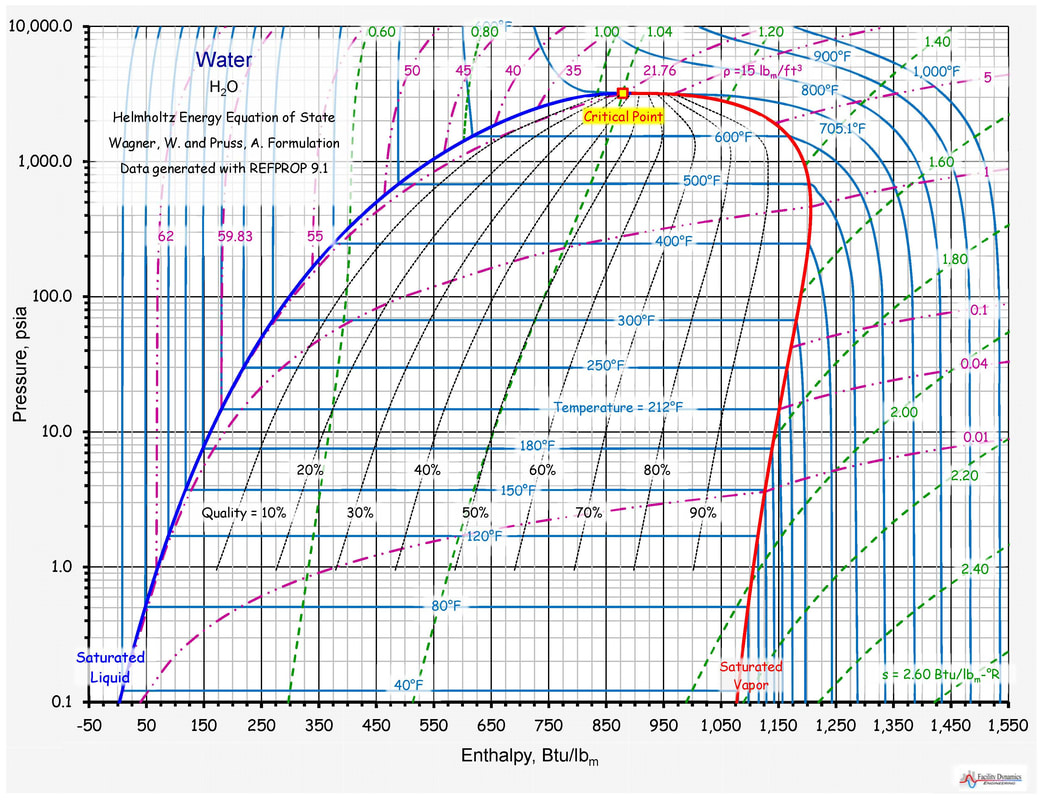
Temperature And Entropy Diagram
PPT Chapter 16 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5604541
thermodynamics How to find the entropy for a given temperature using PH chart for a
Thermodynamics Charts And Tables Pdf Ponasa
Untitled Document [people.chem.umass.edu]
Entropy Is The Disorder Of A System, But That Means A Lot More Than Making A Mess Of A Room.
Entropy Is The Measure Of The Disorder Of A System.
Entropy Is A Scientific Concept, Most Commonly Associated With States Of Disorder, Randomness, Or Uncertainty.
The Second Law Of Thermodynamics States That The Total Entropy Of A System Either Increases Or Remains Constant In Any Spontaneous Process;
Related Post:


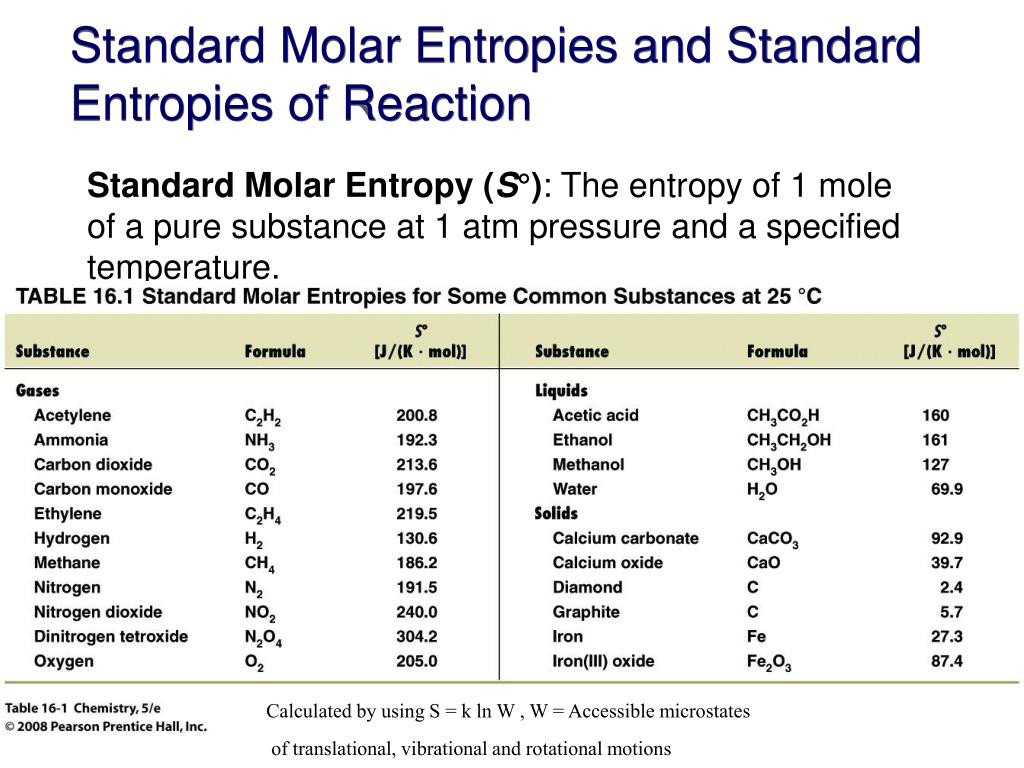

![Untitled Document [people.chem.umass.edu]](https://people.chem.umass.edu/botch/Chem122S08/Chapters/Ch7/Table1AbsoluteEntropies.jpg)