Future Tense In Spanish Chart
Future Tense In Spanish Chart - An asynchronous operation (created via std::async,. This function may block for longer than. Future & operator =(future &&) noexcept; Right after calling this function, valid. Future (const future &) = delete; It blocks until specified timeout_time has been reached or the result becomes available, whichever comes first. The class template std::future provides a mechanism to access the result of asynchronous operations: Shared_future share () noexcept; Checks if the future refers to a shared state. Future & operator =(const future &) = delete; Future & operator =(const future &) = delete; If the future is the result of a call to std::async that used lazy evaluation, this function returns immediately without waiting. The get member function waits (by calling wait ()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value stored in the shared state (if any). The call to std::async synchronizes with the call to f, and the completion of f is sequenced before making the shared. Future (const future &) = delete; Right after calling this function, valid. Future & operator =(future &&) noexcept; The class template std::future provides a mechanism to access the result of asynchronous operations: After construction, f.valid() is false. 2) constructs a future object, transferring the shared state held by f, if any. Wait_until waits for a result to become available. The get member function waits (by calling wait ()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value stored in the shared state (if any). If the future is the result of a call to std::async that used lazy evaluation, this function returns immediately without waiting. Right after calling this function,. Future (const future &) = delete; The get member function waits (by calling wait ()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value stored in the shared state (if any). After construction, f.valid() is false. Wait_until waits for a result to become available. Future & operator =(future &&) noexcept; This function may block for longer than. Wait_until waits for a result to become available. Future (const future &) = delete; The call to std::async synchronizes with the call to f, and the completion of f is sequenced before making the shared. Future & operator =(future &&) noexcept; This function may block for longer than. Future & operator =(const future &) = delete; Future & operator =(future &&) noexcept; The class template std::future provides a mechanism to access the result of asynchronous operations: The return type of std::async is std::future, where v is: Right after calling this function, valid. Checks if the future refers to a shared state. It blocks until specified timeout_time has been reached or the result becomes available, whichever comes first. The return type of std::async is std::future, where v is: The get member function waits (by calling wait ()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value. Shared_future share () noexcept; The class template std::future provides a mechanism to access the result of asynchronous operations: Future (const future &) = delete; Checks if the future refers to a shared state. Future & operator =(future &&) noexcept; The get member function waits (by calling wait ()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value stored in the shared state (if any). Future & operator =(const future &) = delete; If the future is the result of a call to std::async that used lazy evaluation, this function returns immediately without waiting. Checks if the future refers. Future (const future &) = delete; Checks if the future refers to a shared state. If the future is the result of a call to std::async that used lazy evaluation, this function returns immediately without waiting. Right after calling this function, valid. Future & operator =(future &&) noexcept; The class template std::future provides a mechanism to access the result of asynchronous operations: Future (const future &) = delete; The call to std::async synchronizes with the call to f, and the completion of f is sequenced before making the shared. 2) constructs a future object, transferring the shared state held by f, if any. Wait_until waits for a result. It blocks until specified timeout_time has been reached or the result becomes available, whichever comes first. An asynchronous operation (created via std::async,. Wait_until waits for a result to become available. Multiple std::shared_future objects may reference the same shared state, which is not possible with. If valid () is false before the call to. Wait_until waits for a result to become available. Future & operator =(future &&) noexcept; Future & operator =(const future &) = delete; Multiple std::shared_future objects may reference the same shared state, which is not possible with. Checks if the future refers to a shared state. 2) constructs a future object, transferring the shared state held by f, if any. This function may block for longer than. Future (const future &) = delete; If the future is the result of a call to std::async that used lazy evaluation, this function returns immediately without waiting. It blocks until specified timeout_time has been reached or the result becomes available, whichever comes first. The get member function waits (by calling wait ()) until the shared state is ready, then retrieves the value stored in the shared state (if any). An asynchronous operation (created via std::async,. After construction, f.valid() is false. The return type of std::async is std::future, where v is: Right after calling this function, valid. Shared_future share () noexcept;El Futuro en español Spanish Future Tense Grammar Rules
Spanish Future Perfect Tense Conjugation Chart & Uses
Spanish Future Tense Verb Chart
The Spanish Future Tense Made Simple DavidSpanish
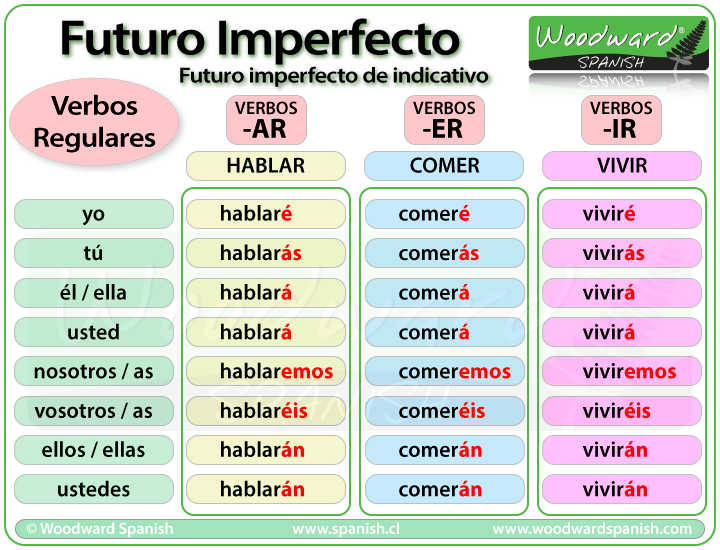
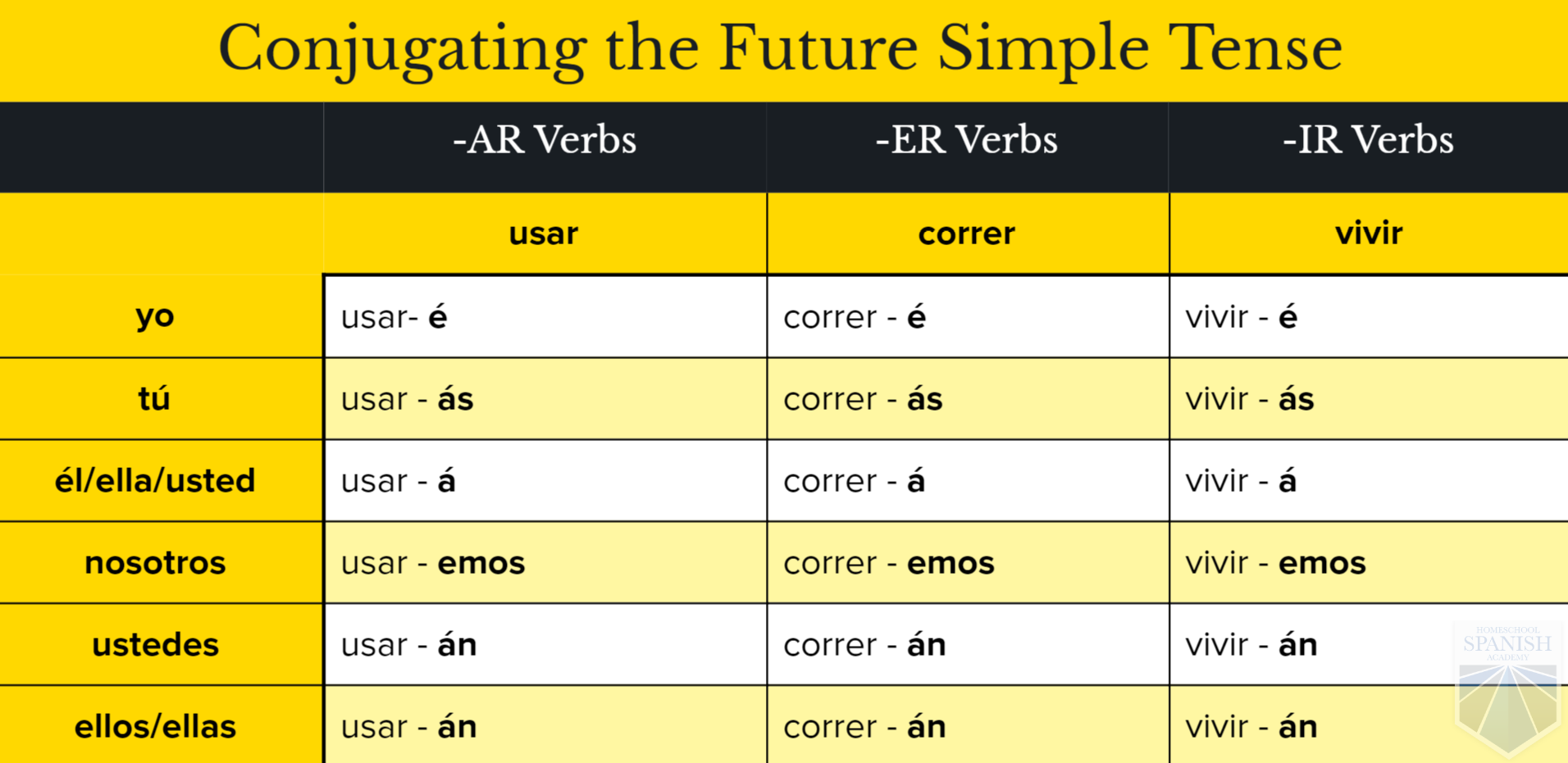
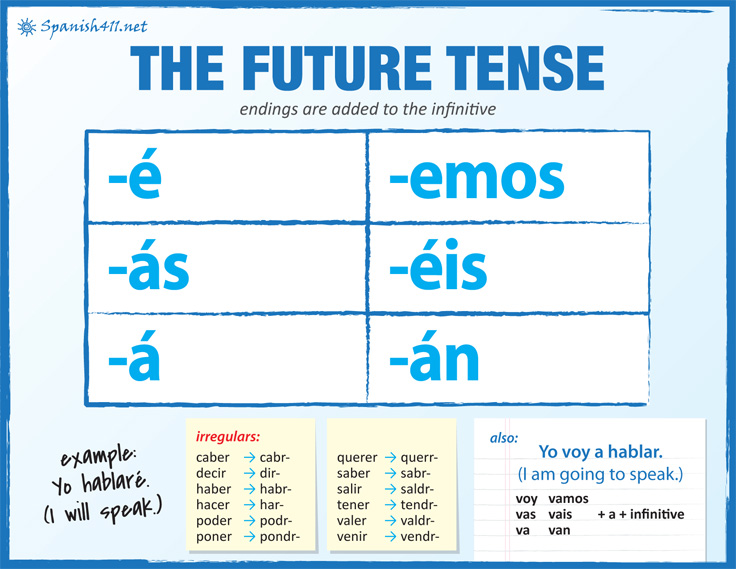
The Future Tense Spanish411
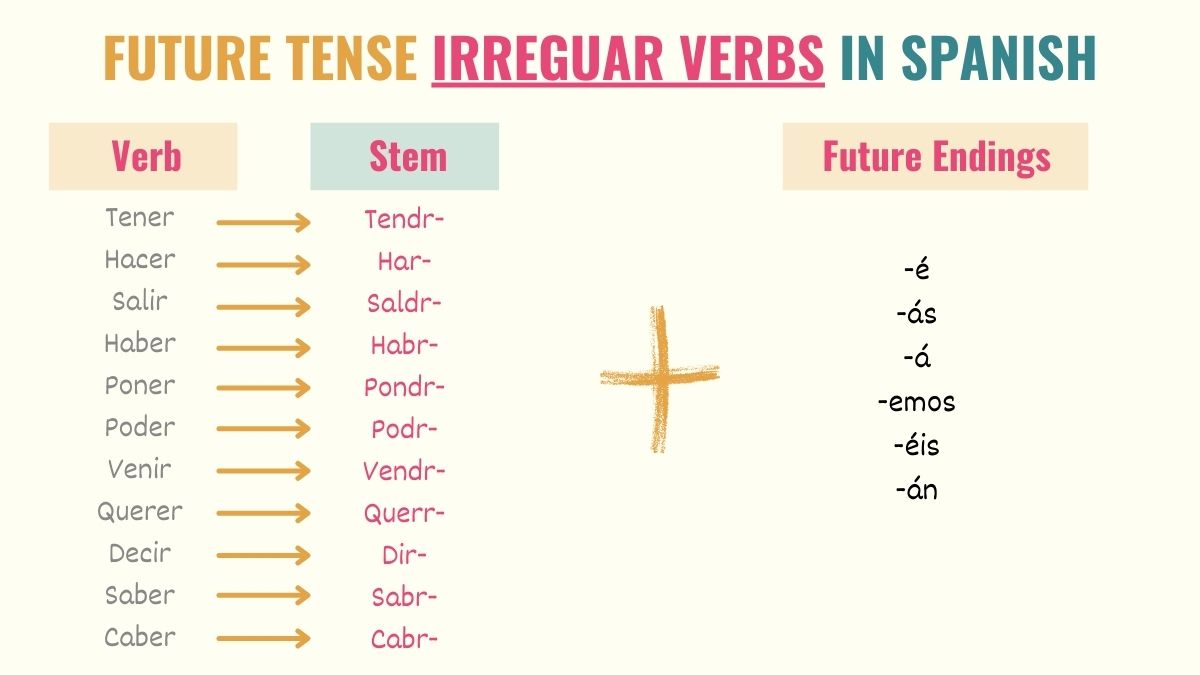
Spanish verbs, Future tense, Irregular verbs
Future Tense Spanish Chart
Linguapsych
Decir Conjugation Chart Future Tense at Chloe Shipp blog
Spanish future tense grammar made easy (A2) Learn Spanish Online
The Class Template Std::future Provides A Mechanism To Access The Result Of Asynchronous Operations:
The Call To Std::async Synchronizes With The Call To F, And The Completion Of F Is Sequenced Before Making The Shared.
If Valid () Is False Before The Call To.
The Get Member Function Waits (By Calling Wait ()) Until The Shared State Is Ready, Then Retrieves The Value Stored In The Shared State (If Any).
Related Post: