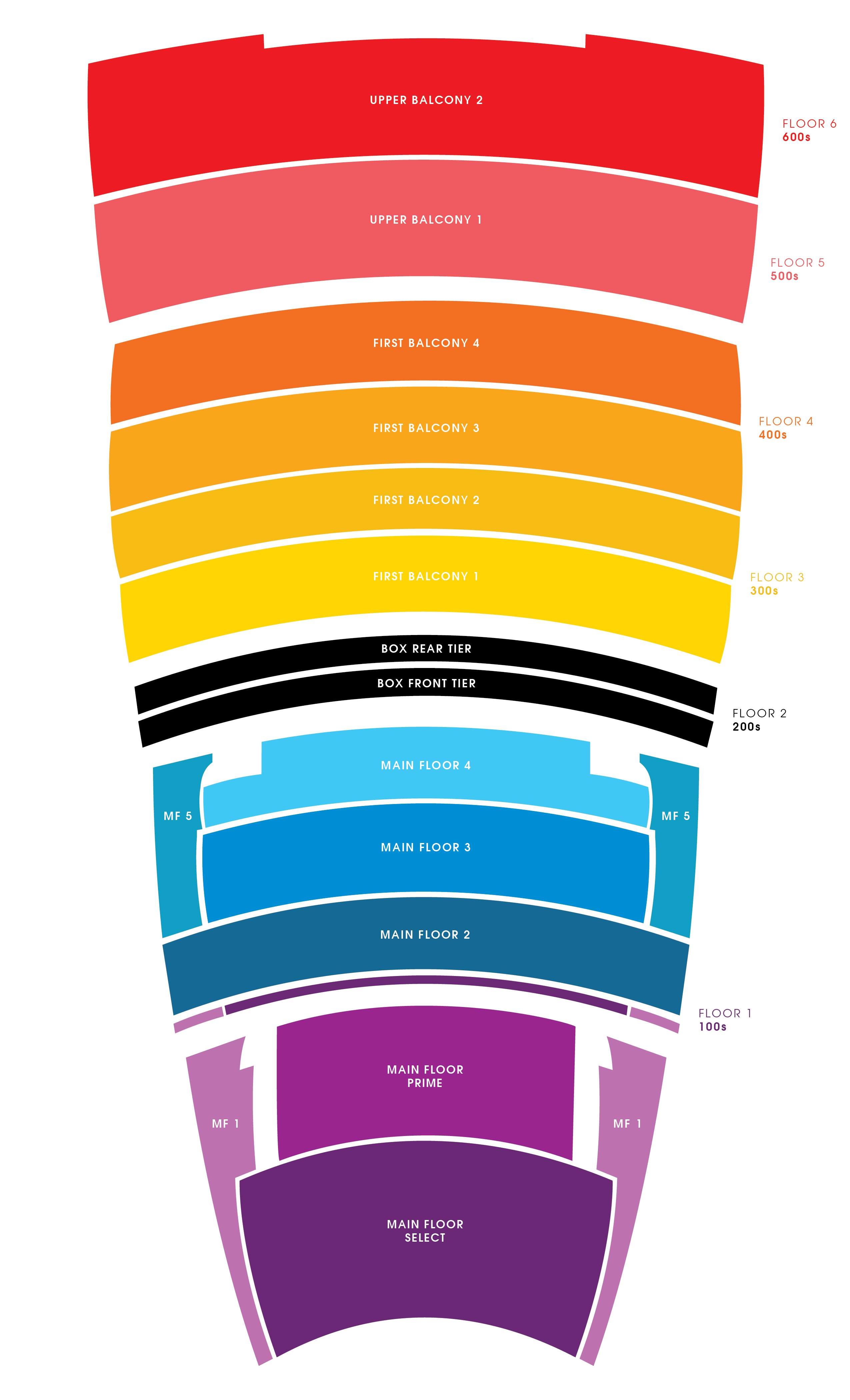
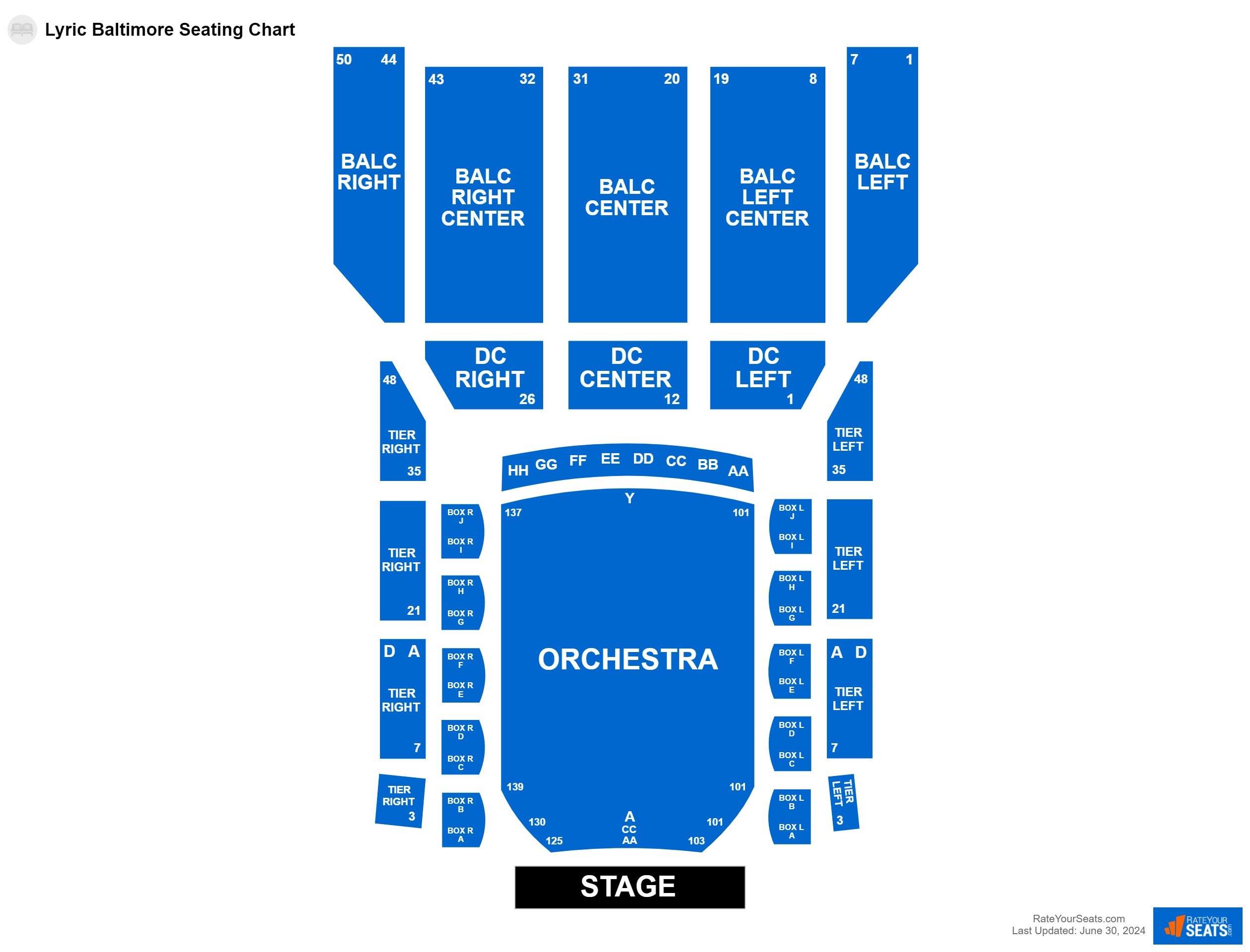
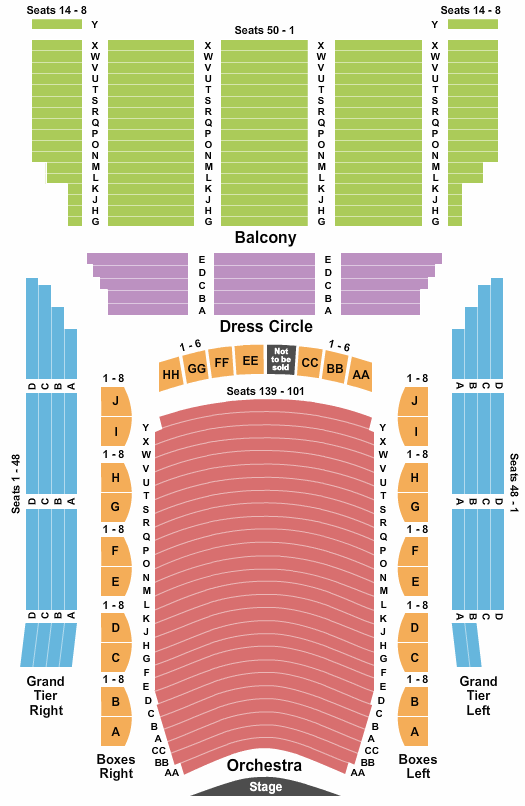
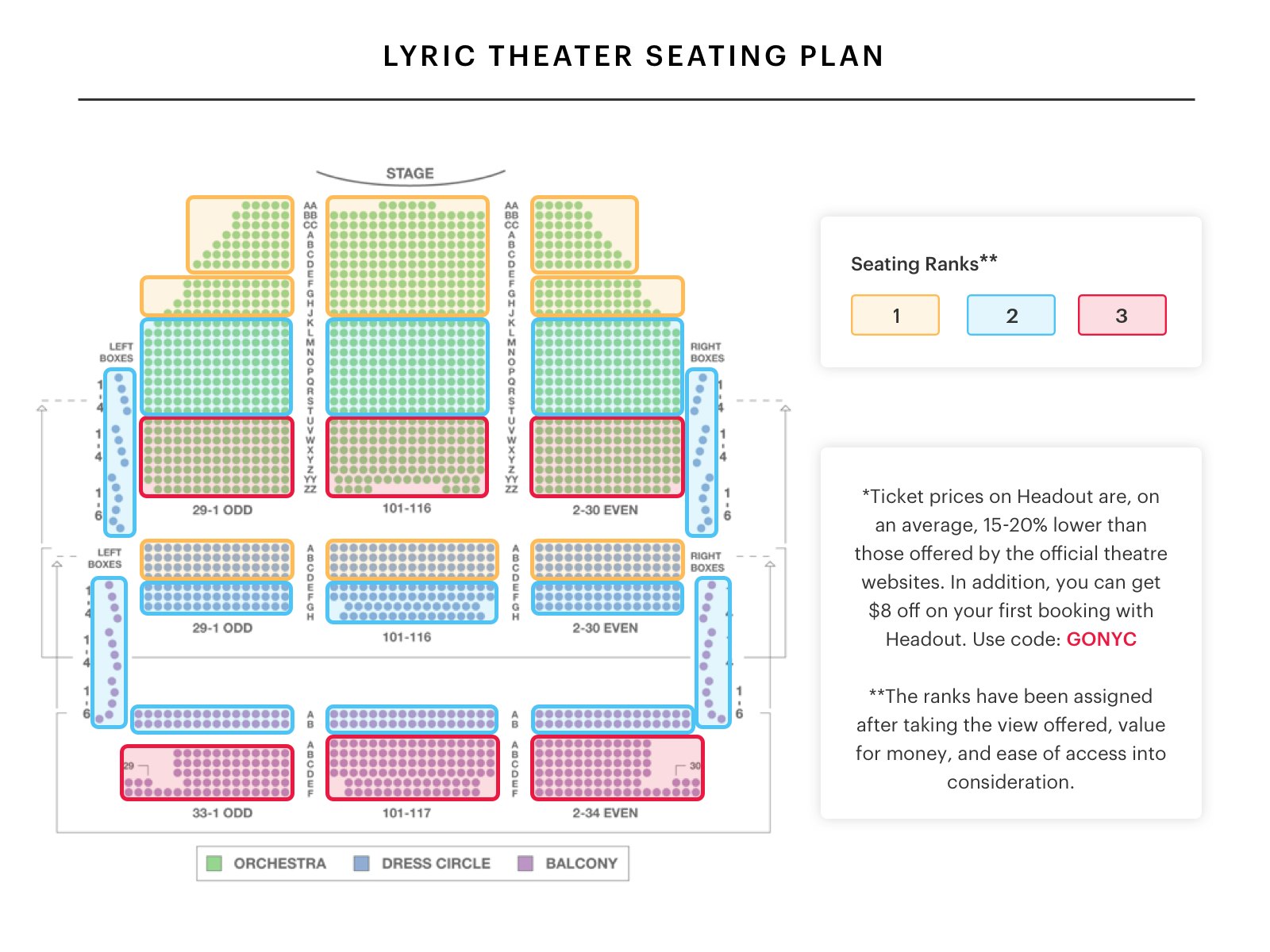
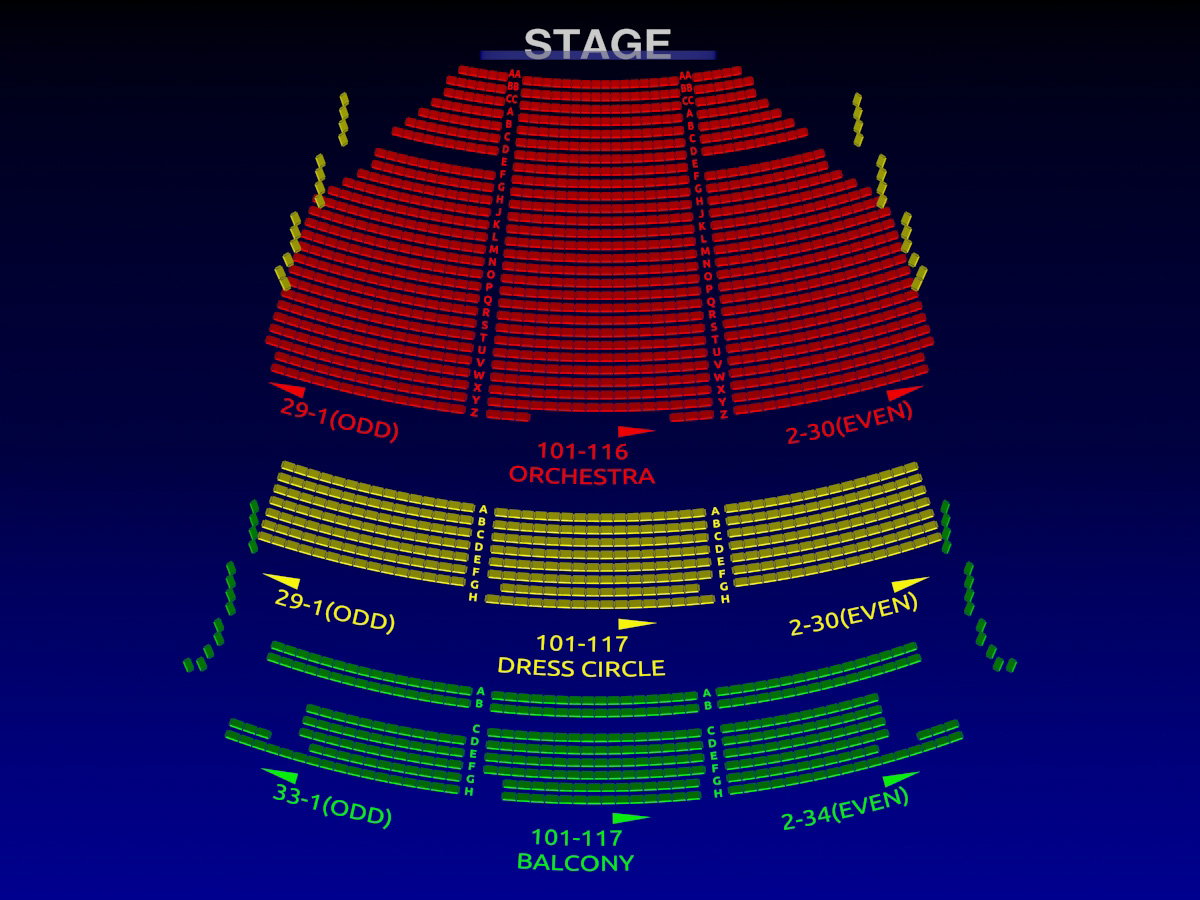
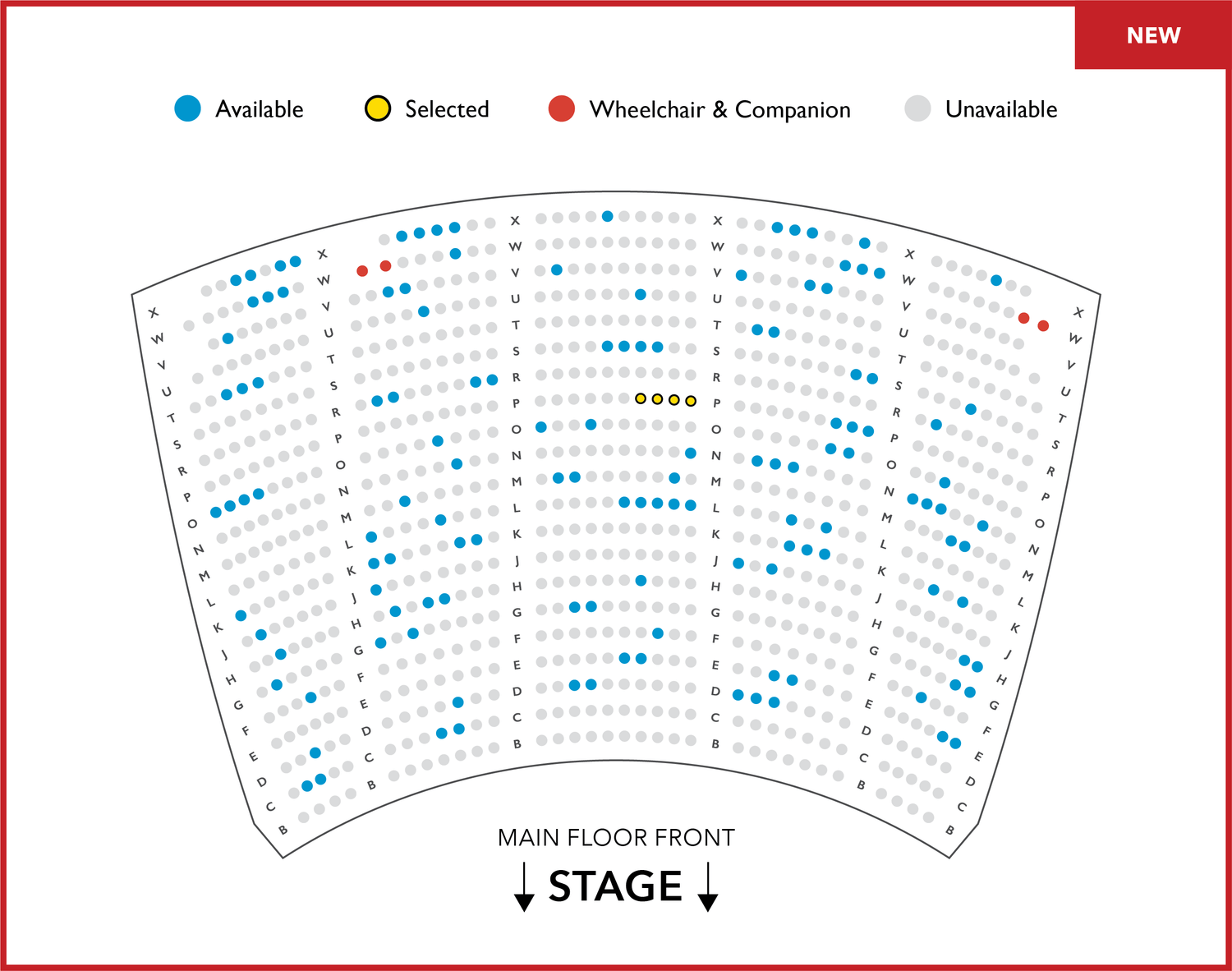
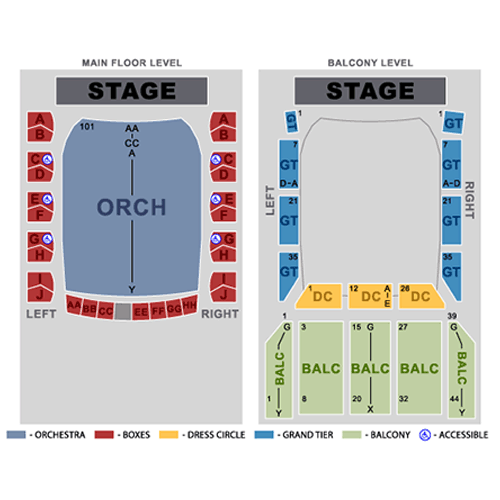
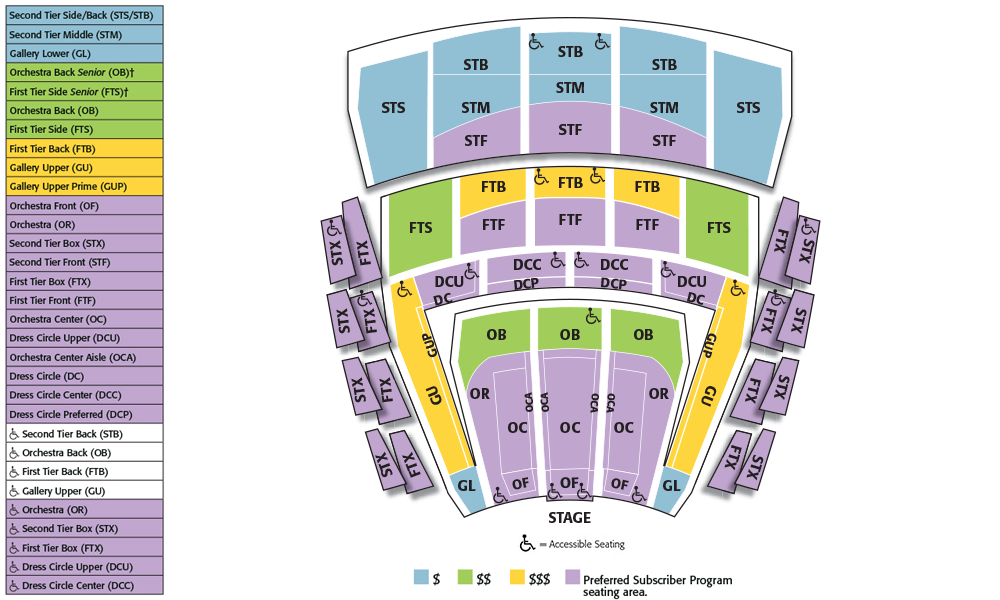
Lyric Opera House Baltimore Seating Chart
Lyric Opera House Baltimore Seating Chart - The concentration of the reactants. In a few cases, increasing the concentration of one of the. Increasing the concentration of reactants generally increases the rate of reaction because more of the reacting molecules or ions are present to form the reaction products. Conversely, the lower the concentration, the slower the reaction rate. The reaction orders state in practical terms that doubling the concentration of (ch 3) 3 cbr doubles the reaction rate of the hydrolysis reaction, halving the concentration of (ch. The chemical nature of the reacting substances, the state of subdivision (one large lump versus many small particles) of. For example, consider a reaction mechanism where the rate. In going from experiment 2 to 3 we doubled the concentration of [b] at constant [a], [c] and the reaction went 8 times as fast, so the order with respect to b is 3, as 2 3 =8. The results show that the higher the concentration, the faster the reaction rate. There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction: For example, consider a reaction mechanism where the rate. There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction: The reaction orders state in practical terms that doubling the concentration of (ch 3) 3 cbr doubles the reaction rate of the hydrolysis reaction, halving the concentration of (ch. For many reactions involving liquids or gases, increasing the concentration of the reactants increases the rate of reaction. In a few cases, increasing the concentration of one of the. Increasing the concentration of reactants generally increases the rate of reaction because more of the reacting molecules or ions are present to form the reaction products. In going from experiment 2 to 3 we doubled the concentration of [b] at constant [a], [c] and the reaction went 8 times as fast, so the order with respect to b is 3, as 2 3 =8. The more concentrated the faster the rate. The results show that the higher the concentration, the faster the reaction rate. By measuring how the rate changes with varying concentrations of reactants, the orders of reaction can be deduced. By measuring how the rate changes with varying concentrations of reactants, the orders of reaction can be deduced. For many reactions involving liquids or gases, increasing the concentration of the reactants increases the rate of reaction. In going from experiment 2 to 3 we doubled the concentration of [b] at constant [a], [c] and the reaction went 8 times as. Conversely, the lower the concentration, the slower the reaction rate. For many reactions involving liquids or gases, increasing the concentration of the reactants increases the rate of reaction. The chemical nature of the reacting substances, the state of subdivision (one large lump versus many small particles) of. The reaction orders state in practical terms that doubling the concentration of (ch. In a few cases, increasing the concentration of one of the. There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction: The more concentrated the faster the rate. While c is present in the reaction, its concentration does not appear in the rate law equation. By measuring how the rate changes with varying concentrations of reactants, the. There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction: Let’s use 3 m and 6 m for the concentration of a and see how that affects the rate of. The chemical nature of the reacting substances, the state of subdivision (one large lump versus many small particles) of. While c is present in the reaction, its. There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction: In going from experiment 2 to 3 we doubled the concentration of [b] at constant [a], [c] and the reaction went 8 times as fast, so the order with respect to b is 3, as 2 3 =8. The results show that the higher the concentration, the. In going from experiment 2 to 3 we doubled the concentration of [b] at constant [a], [c] and the reaction went 8 times as fast, so the order with respect to b is 3, as 2 3 =8. For many reactions involving liquids or gases, increasing the concentration of the reactants increases the rate of reaction. The concentration of the. The chemical nature of the reacting substances, the state of subdivision (one large lump versus many small particles) of. The more concentrated the faster the rate. There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction: For example, consider a reaction mechanism where the rate. The reaction orders state in practical terms that doubling the concentration of. Five factors typically determine the speed of chemical reactions: For many reactions involving liquids or gases, increasing the concentration of the reactants increases the rate of reaction. The results show that the higher the concentration, the faster the reaction rate. The concentration of the reactants. Conversely, the lower the concentration, the slower the reaction rate. Five factors typically determine the speed of chemical reactions: In a few cases, increasing the concentration of one of the. The chemical nature of the reacting substances, the state of subdivision (one large lump versus many small particles) of. The results show that the higher the concentration, the faster the reaction rate. The concentration of the reactants. By measuring how the rate changes with varying concentrations of reactants, the orders of reaction can be deduced. Let’s use 3 m and 6 m for the concentration of a and see how that affects the rate of. There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction: In going from experiment 2 to 3 we doubled. While c is present in the reaction, its concentration does not appear in the rate law equation. Five factors typically determine the speed of chemical reactions: Conversely, the lower the concentration, the slower the reaction rate. The reaction orders state in practical terms that doubling the concentration of (ch 3) 3 cbr doubles the reaction rate of the hydrolysis reaction, halving the concentration of (ch. The more concentrated the faster the rate. The results show that the higher the concentration, the faster the reaction rate. Let’s use 3 m and 6 m for the concentration of a and see how that affects the rate of. In a few cases, increasing the concentration of one of the. There are five general properties that can affect the rate of a reaction: For example, consider a reaction mechanism where the rate. The concentration of the reactants. For many reactions involving liquids or gases, increasing the concentration of the reactants increases the rate of reaction.Lyric Opera Seating Chart Lyric opera seating chart
The Opera House Seating Chart
Stephen Sharer Baltimore Event Tickets Lyric Opera House
Lyric Opera House Seating Chart Baltimore Md Congratulations Everyone
Lyric opera house baltimore seating chart headver
Lyric Theatre Broadway Seating Chart Broadway Scene
Lyric Opera Chicago Seating
The Lyric Baltimore Seating Chart Portal.posgradount.edu.pe
Lyric Opera House Seating Chart Baltimore
Lyric Opera House Baltimore Seating Chart Portal.posgradount.edu.pe
In Going From Experiment 2 To 3 We Doubled The Concentration Of [B] At Constant [A], [C] And The Reaction Went 8 Times As Fast, So The Order With Respect To B Is 3, As 2 3 =8.
Increasing The Concentration Of Reactants Generally Increases The Rate Of Reaction Because More Of The Reacting Molecules Or Ions Are Present To Form The Reaction Products.
By Measuring How The Rate Changes With Varying Concentrations Of Reactants, The Orders Of Reaction Can Be Deduced.
The Chemical Nature Of The Reacting Substances, The State Of Subdivision (One Large Lump Versus Many Small Particles) Of.
Related Post: