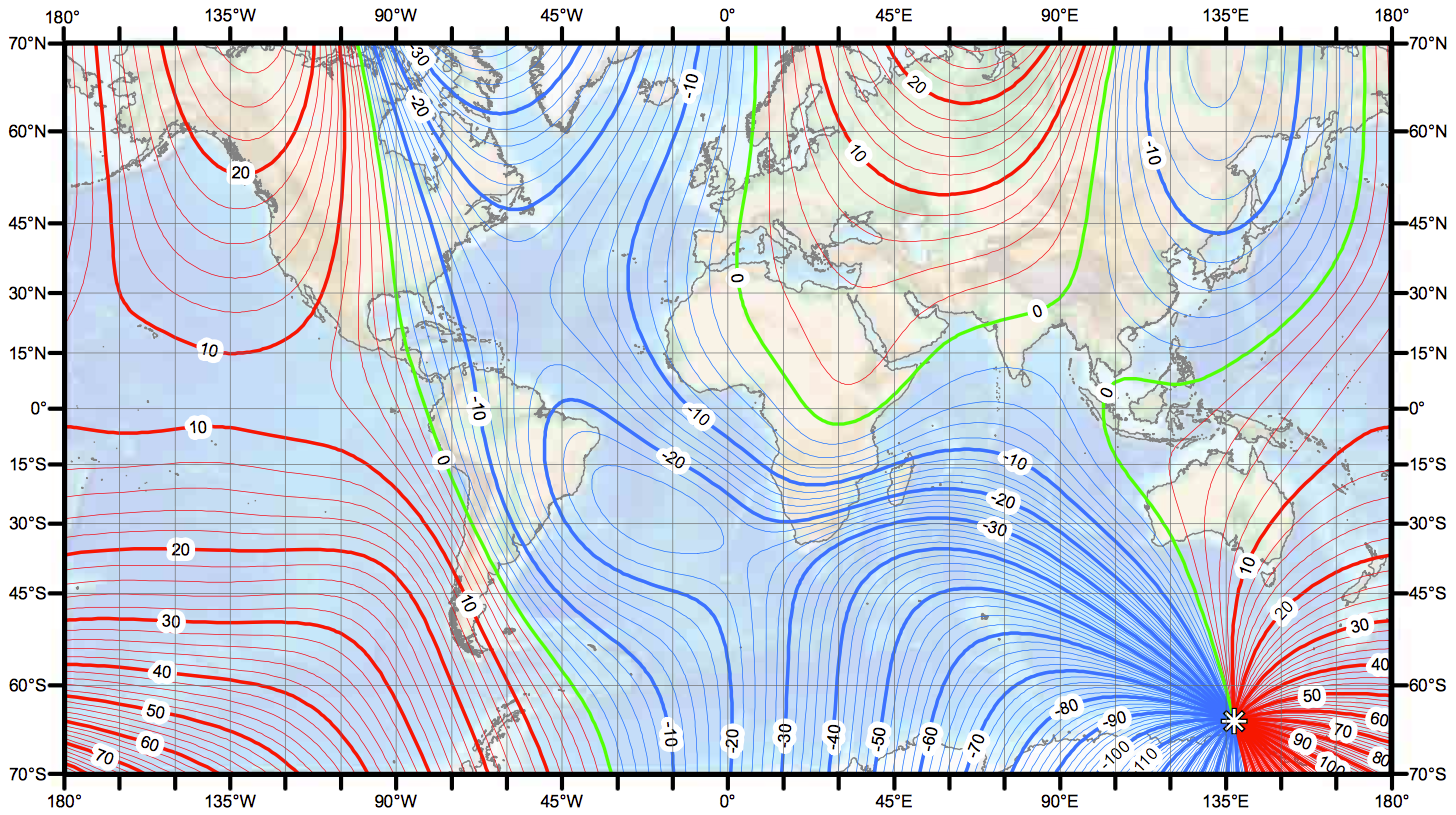
Magnetic Variation Chart
Magnetic Variation Chart - Of, pertaining to, or being a medium created with. Having the properties of a magnet. Magnetism, phenomenon associated with magnetic fields, which arise from the motion of electric charges. The force acting on an electrically charged particle in a magnetic field depends on the magnitude of the charge, the velocity of the particle, and the strength of the magnetic field. Although ferromagnetic materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one. Magnetic refers to the property or behavior of an object that is attracted to a magnet or can produce a magnetic field itself. Learn the definition of magnetism, discover the types of magnetic materials, and get interesting magnetism facts. Hear the chilling sounds of earth’s north and south poles reversing 780k years ago — could it happen again? Magnets are objects that produce magnetic fields and attract metals like iron, nickel and cobalt. How to use magnetic in a sentence. Although ferromagnetic materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one. Capable of being magnetized or attracted by a magnet. It also relates to the force that electric currents and magnetic materials exert. It can be an electric current in a conductor or charged particles moving. The magnetic field's lines of force exit the magnet from its north pole and enter its. How to use magnetic in a sentence. The meaning of magnetic is possessing an extraordinary power or ability to attract. Of, pertaining to, or being a medium created with. Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Magnetism, phenomenon associated with magnetic fields, which arise from the motion of electric charges. It also relates to the force that electric currents and magnetic materials exert. It can be an electric current in a conductor or charged particles moving. Of, pertaining to, or being a medium created with. The meaning of magnetic is possessing an extraordinary power or ability to attract. Hear the chilling sounds of earth’s north and south poles reversing 780k. Magnets are objects that produce magnetic fields and attract metals like iron, nickel and cobalt. Although ferromagnetic materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one. It can be an electric current in a conductor or charged particles moving. The meaning of. Hear the chilling sounds of earth’s north and south poles reversing 780k years ago — could it happen again? It also relates to the force that electric currents and magnetic materials exert. Learn the definition of magnetism, discover the types of magnetic materials, and get interesting magnetism facts. The force acting on an electrically charged particle in a magnetic field. Having the properties of a magnet. How to use magnetic in a sentence. Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. The magnetic field's lines of force exit the magnet from its north pole and enter its. It can be an electric current in a conductor. Having the properties of a magnet. Magnetism, phenomenon associated with magnetic fields, which arise from the motion of electric charges. How to use magnetic in a sentence. The force acting on an electrically charged particle in a magnetic field depends on the magnitude of the charge, the velocity of the particle, and the strength of the magnetic field. Although ferromagnetic. It can be an electric current in a conductor or charged particles moving. Having the properties of a magnet. Hear the chilling sounds of earth’s north and south poles reversing 780k years ago — could it happen again? Although ferromagnetic materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond. It also relates to the force that electric currents and magnetic materials exert. Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Hear the chilling sounds of earth’s north and south poles reversing 780k years ago — could it happen again? Although ferromagnetic materials are the only. The magnetic field's lines of force exit the magnet from its north pole and enter its. It can be an electric current in a conductor or charged particles moving. Hear the chilling sounds of earth’s north and south poles reversing 780k years ago — could it happen again? Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of. How to use magnetic. Hear the chilling sounds of earth’s north and south poles reversing 780k years ago — could it happen again? Learn the definition of magnetism, discover the types of magnetic materials, and get interesting magnetism facts. Magnets are objects that produce magnetic fields and attract metals like iron, nickel and cobalt. The meaning of magnetic is possessing an extraordinary power or. Hear the chilling sounds of earth’s north and south poles reversing 780k years ago — could it happen again? Learn the definition of magnetism, discover the types of magnetic materials, and get interesting magnetism facts. Magnets are objects that produce magnetic fields and attract metals like iron, nickel and cobalt. The meaning of magnetic is possessing an extraordinary power or. Having the properties of a magnet. Learn the definition of magnetism, discover the types of magnetic materials, and get interesting magnetism facts. Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. It also relates to the force that electric currents and magnetic materials exert. Magnetism, phenomenon associated with magnetic fields, which arise from the motion of electric charges. How to use magnetic in a sentence. Capable of being magnetized or attracted by a magnet. Magnetic refers to the property or behavior of an object that is attracted to a magnet or can produce a magnetic field itself. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of. It can be an electric current in a conductor or charged particles moving. The meaning of magnetic is possessing an extraordinary power or ability to attract. Magnets are objects that produce magnetic fields and attract metals like iron, nickel and cobalt. The magnetic field's lines of force exit the magnet from its north pole and enter its. The force acting on an electrically charged particle in a magnetic field depends on the magnitude of the charge, the velocity of the particle, and the strength of the magnetic field.Fig. 1 Variation Chart.
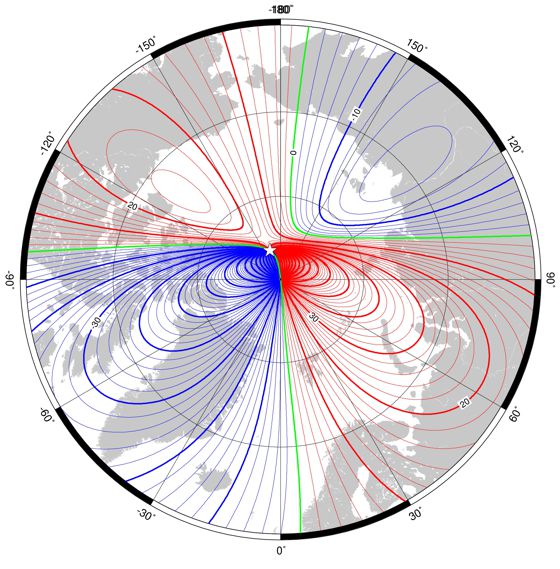
Global Models
Compass Declination Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
PPT Instruments part 1 PowerPoint Presentation ID459014
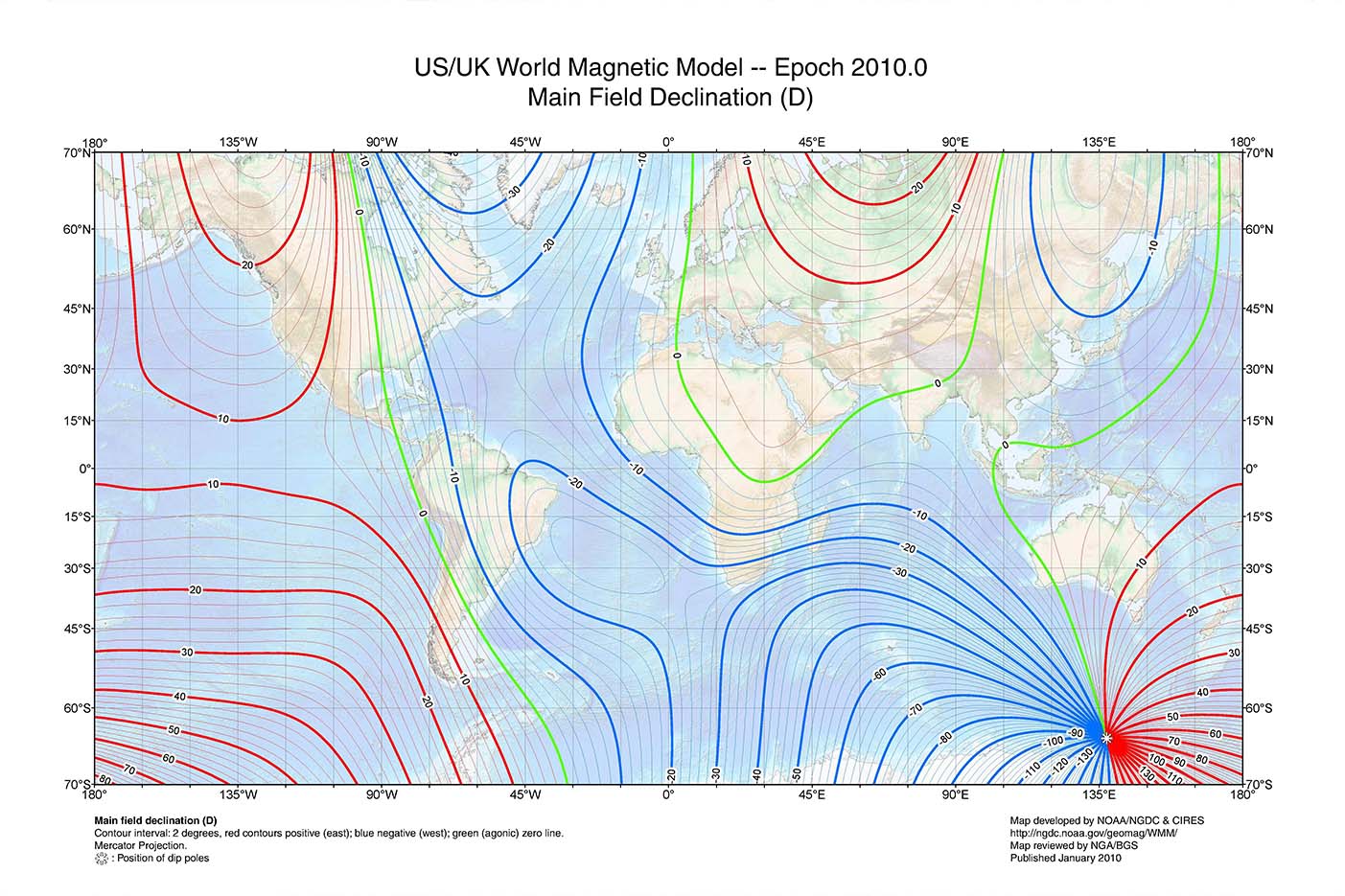
World Model (WMM) National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI)
GeoGarage blog World Model updated
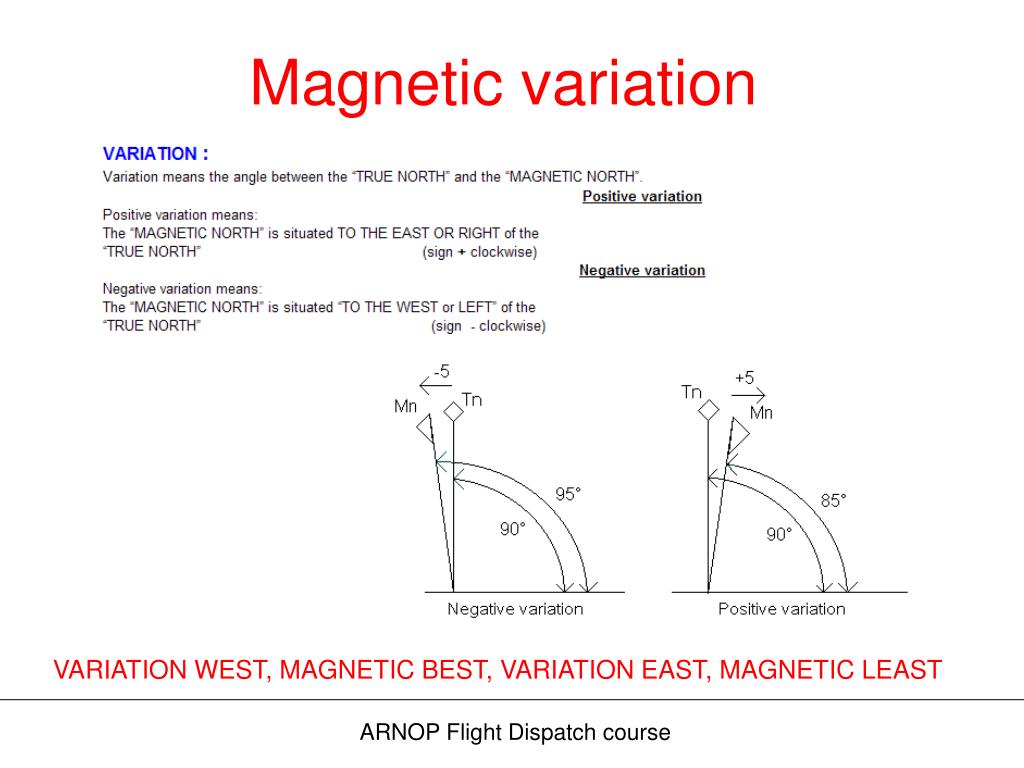
navigation How can I use a declination chart to calculate true track, track
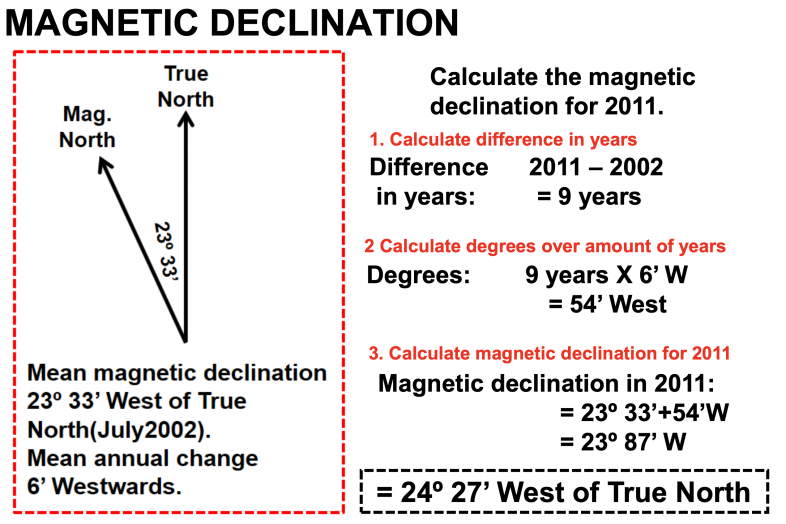
How to Calculate Declination in Geography » My Courses
Understanding Declination Science! Astronomy & Space Exploration, and Others Cloudy
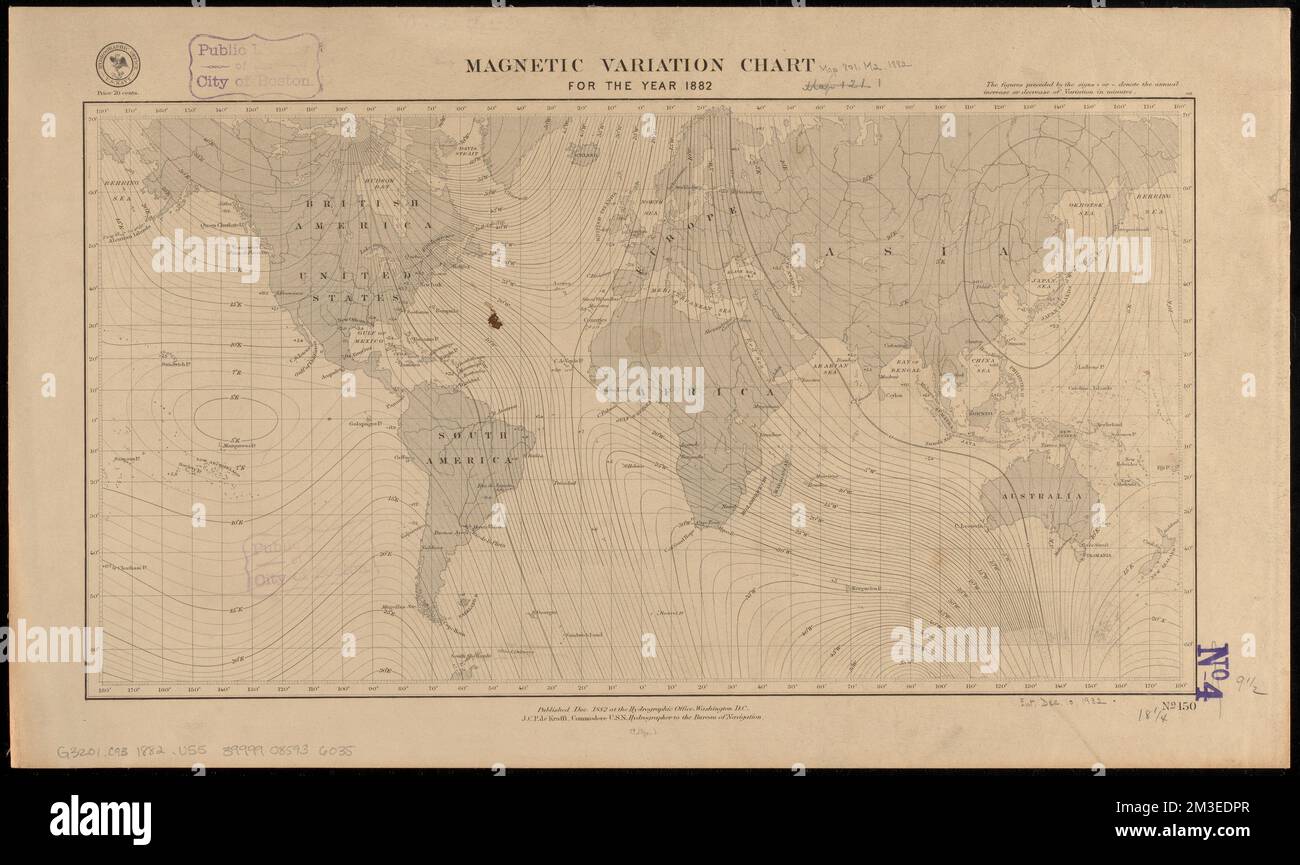
variation chart for the year 1882 , declination, Maps, World maps Norman B
Of, Pertaining To, Or Being A Medium Created With.
Although Ferromagnetic Materials Are The Only Ones Attracted To A Magnet Strongly Enough To Be Commonly Considered Magnetic, All Other Substances Respond Weakly To A Magnetic Field, By One.
Of Or Pertaining To A Magnet Or Magnetism.
Hear The Chilling Sounds Of Earth’s North And South Poles Reversing 780K Years Ago — Could It Happen Again?
Related Post:
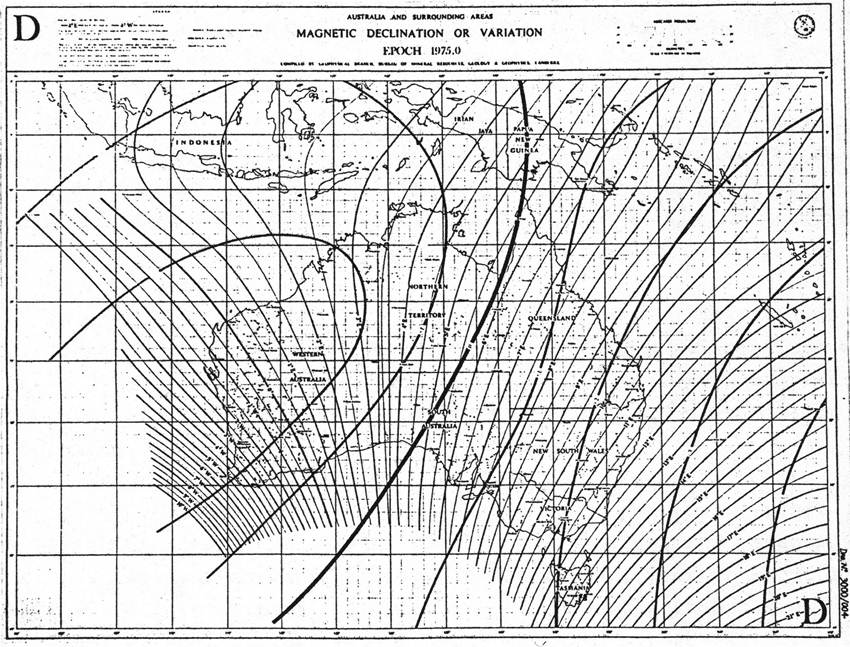
.jpg)