Periodontal Prognosis Chart
Periodontal Prognosis Chart - Periodontal (gum) diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, are largely preventable and treatable. The goal of periodontal treatment is to eliminate dysbiotic plaque biofilm from the tooth surface and to establish an environment that allows the maintenance of health. Periodontitis is a serious infection of the gums caused by bacteria that have been allowed to accumulate on your teeth and gums. Symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath and loose teeth. Periodontal disease (pd) can be described as an inflammatory condition affecting the supporting structures of the teeth. As periodontitis progresses, your bones and. Periodontal disease encompasses inflammatory conditions affecting the periodontium—the gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone. Without treatment, the alveolar bone around the teeth will. Periodontal disease refers to inflammation and infection of the tissues that support your teeth. This condition—which is common among. Periodontal (gum) disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. Studies have shown that pd is associated with higher levels of. Periodontal disease (pd) can be described as an inflammatory condition affecting the supporting structures of the teeth. The goal of periodontal treatment is to eliminate dysbiotic plaque biofilm from the tooth surface and to establish an environment that allows the maintenance of health. It's typically caused by poor brushing and flossing habits that allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to. Periodontitis (gum disease) occurs when the gums become infected and inflamed due to a buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Periodontal (gum) diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, are largely preventable and treatable. Without treatment, the alveolar bone around the teeth will. Symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath and loose teeth. Periodontitis is a serious infection of the gums caused by bacteria that have been allowed to accumulate on your teeth and gums. Periodontal (gum) diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, are largely preventable and treatable. Periodontitis is a serious infection of the gums caused by bacteria that have been allowed to accumulate on your teeth and gums. As periodontitis progresses, your bones and. Periodontal disease (pd) can be described as an inflammatory condition affecting the supporting structures of the teeth. Periodontal disease. Periodontitis (gum disease) occurs when the gums become infected and inflamed due to a buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. This condition—which is common among. As periodontitis progresses, your bones and. Periodontal (gum) disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. Periodontitis is a serious infection of the gums caused by bacteria that. Studies have shown that pd is associated with higher levels of. Periodontal (gum) diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, are largely preventable and treatable. Periodontitis, or gum disease, is a common infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. The goal of periodontal treatment is to eliminate dysbiotic plaque biofilm from the tooth surface and to establish. The goal of periodontal treatment is to eliminate dysbiotic plaque biofilm from the tooth surface and to establish an environment that allows the maintenance of health. Symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath and loose teeth. Periodontitis (gum disease) occurs when the gums become infected and inflamed due to a buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. As periodontitis progresses,. Symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath and loose teeth. Periodontal (gum) disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. This condition—which is common among. Periodontitis is a serious infection of the gums caused by bacteria that have been allowed to accumulate on your teeth and gums. The goal of periodontal treatment is to eliminate dysbiotic. Studies have shown that pd is associated with higher levels of. This condition—which is common among. Periodontal (gum) disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. The goal of periodontal treatment is to eliminate dysbiotic plaque biofilm from the tooth surface and to establish an environment that allows the maintenance of health. Periodontitis is a. Periodontitis (gum disease) occurs when the gums become infected and inflamed due to a buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Periodontal disease (pd) can be described as an inflammatory condition affecting the supporting structures of the teeth. The goal of periodontal treatment is to eliminate dysbiotic plaque biofilm from the tooth surface and to establish an environment that. Periodontal disease refers to inflammation and infection of the tissues that support your teeth. This condition—which is common among. The goal of periodontal treatment is to eliminate dysbiotic plaque biofilm from the tooth surface and to establish an environment that allows the maintenance of health. Symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath and loose teeth. Without treatment, the alveolar bone around. As periodontitis progresses, your bones and. Symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath and loose teeth. Periodontal disease (pd) can be described as an inflammatory condition affecting the supporting structures of the teeth. Periodontitis is a serious infection of the gums caused by bacteria that have been allowed to accumulate on your teeth and gums. Periodontal (gum) diseases, such as gingivitis. As periodontitis progresses, your bones and. Periodontitis is a serious infection of the gums caused by bacteria that have been allowed to accumulate on your teeth and gums. Periodontitis, or gum disease, is a common infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. Without treatment, the alveolar bone around the teeth will. Periodontal (gum) disease is an. Symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath and loose teeth. Periodontitis is a serious infection of the gums caused by bacteria that have been allowed to accumulate on your teeth and gums. Periodontal disease encompasses inflammatory conditions affecting the periodontium—the gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone. Without treatment, the alveolar bone around the teeth will. It's typically caused by poor brushing and flossing habits that allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to. Periodontal (gum) disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. This condition—which is common among. Periodontal disease (pd) can be described as an inflammatory condition affecting the supporting structures of the teeth. Studies have shown that pd is associated with higher levels of. Periodontitis, or gum disease, is a common infection that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. As periodontitis progresses, your bones and. Periodontal disease refers to inflammation and infection of the tissues that support your teeth.New classification of periodontal diseases Zerodonto Dentistry in Blog
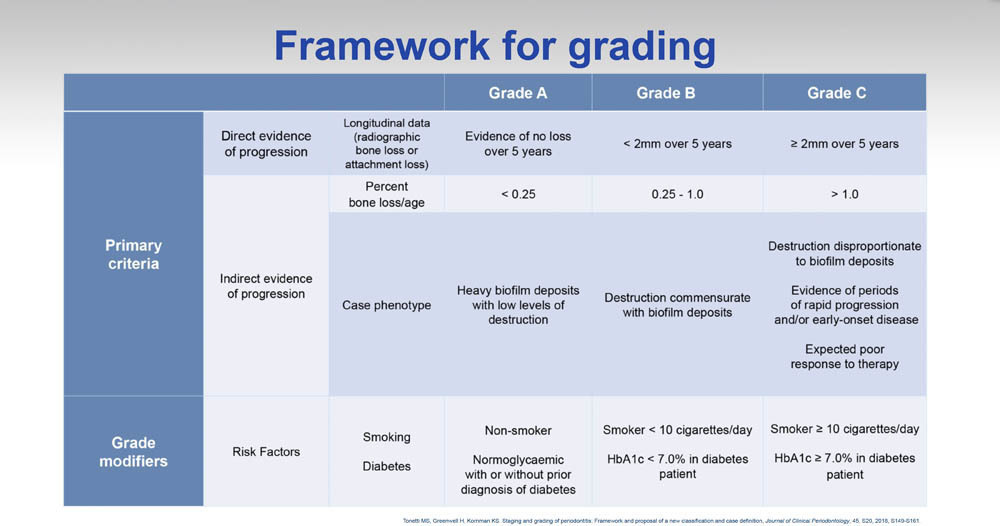
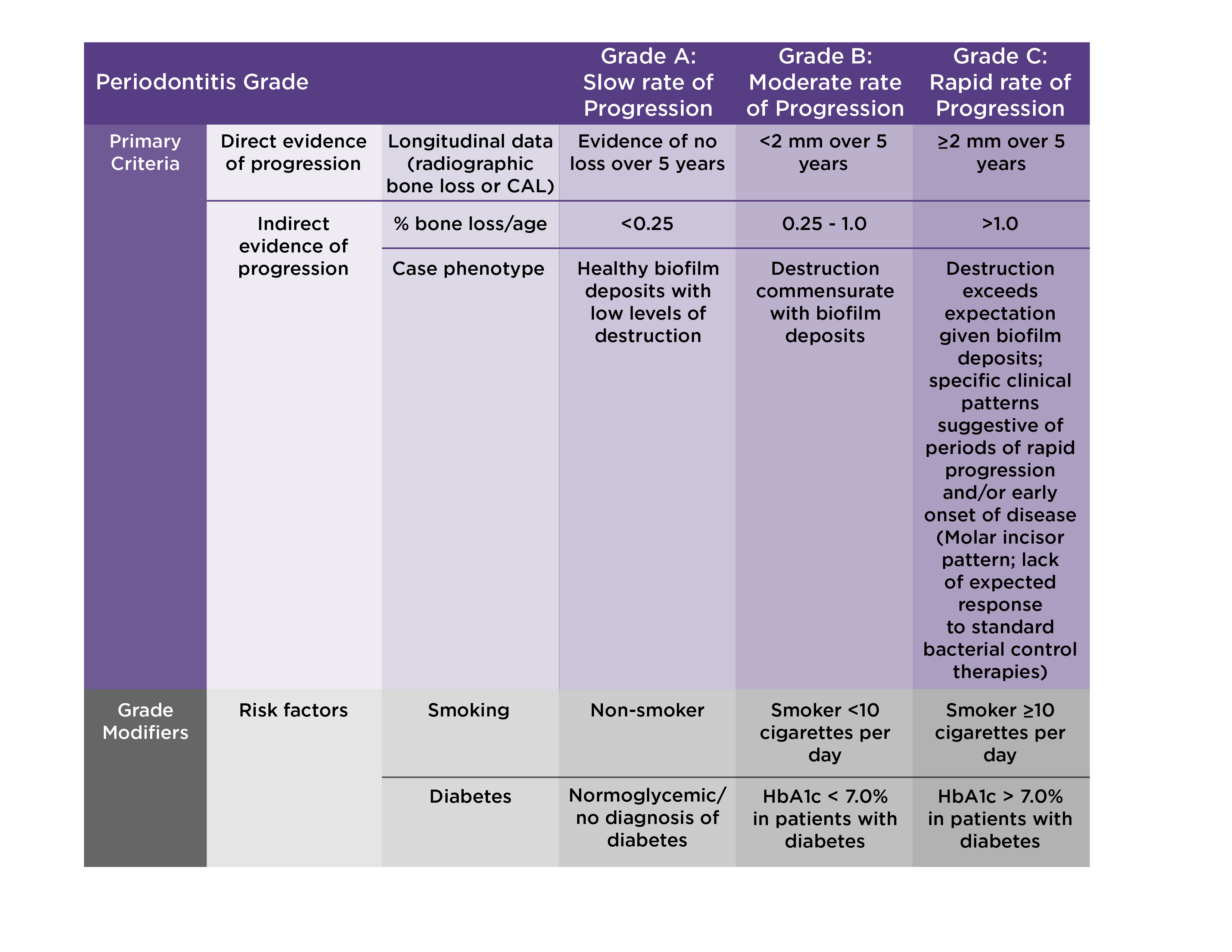
Periodontal Disease Stages Staging and Grading Periodontal Therapy
Periodontal Disease Stages Staging and Grading Periodontal Therapy
Periodontitis Staging and Grading Oral Health Group
Strategies for Periodontal Risk Assessment and Prognosis Decisions in Dentistry
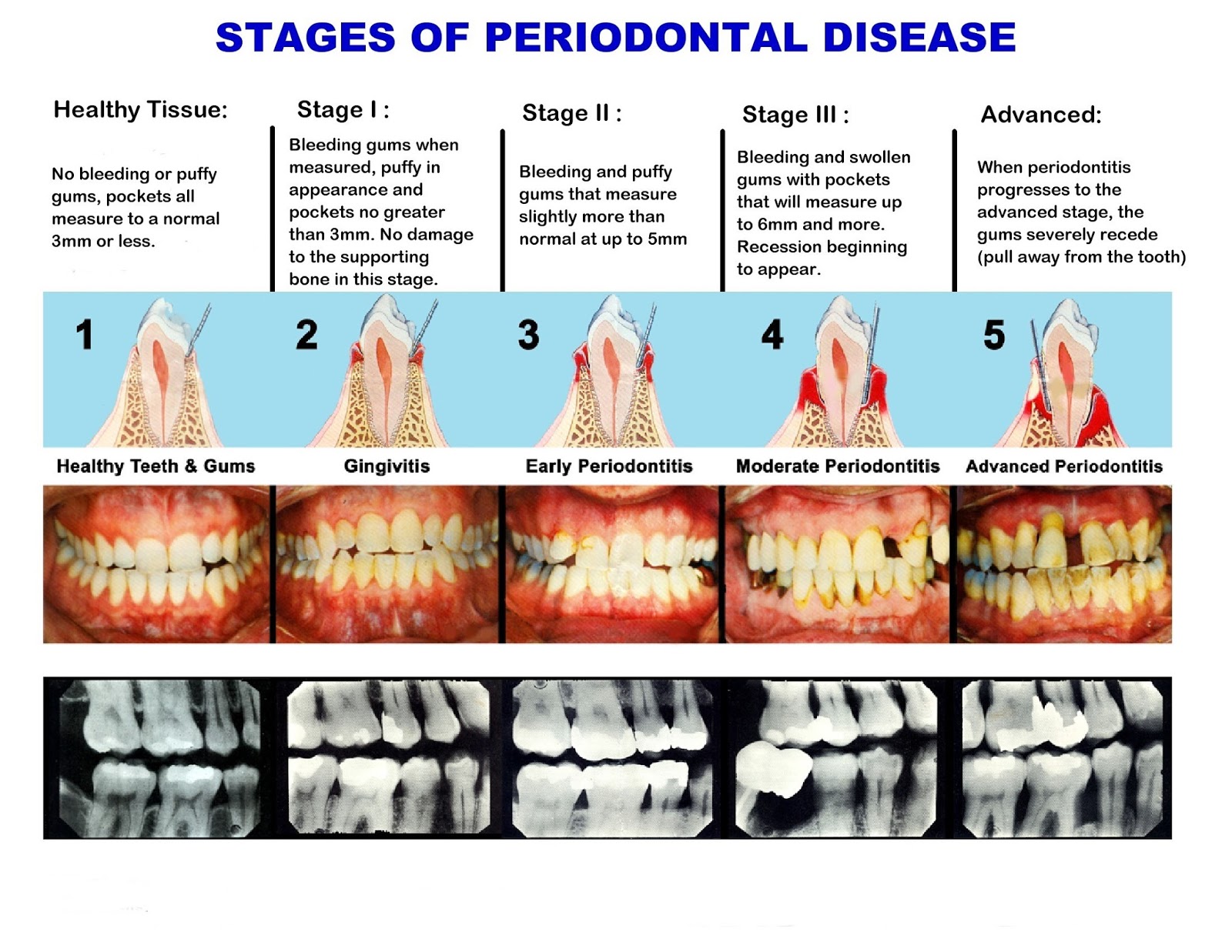
Full Periodontal Charting Explained
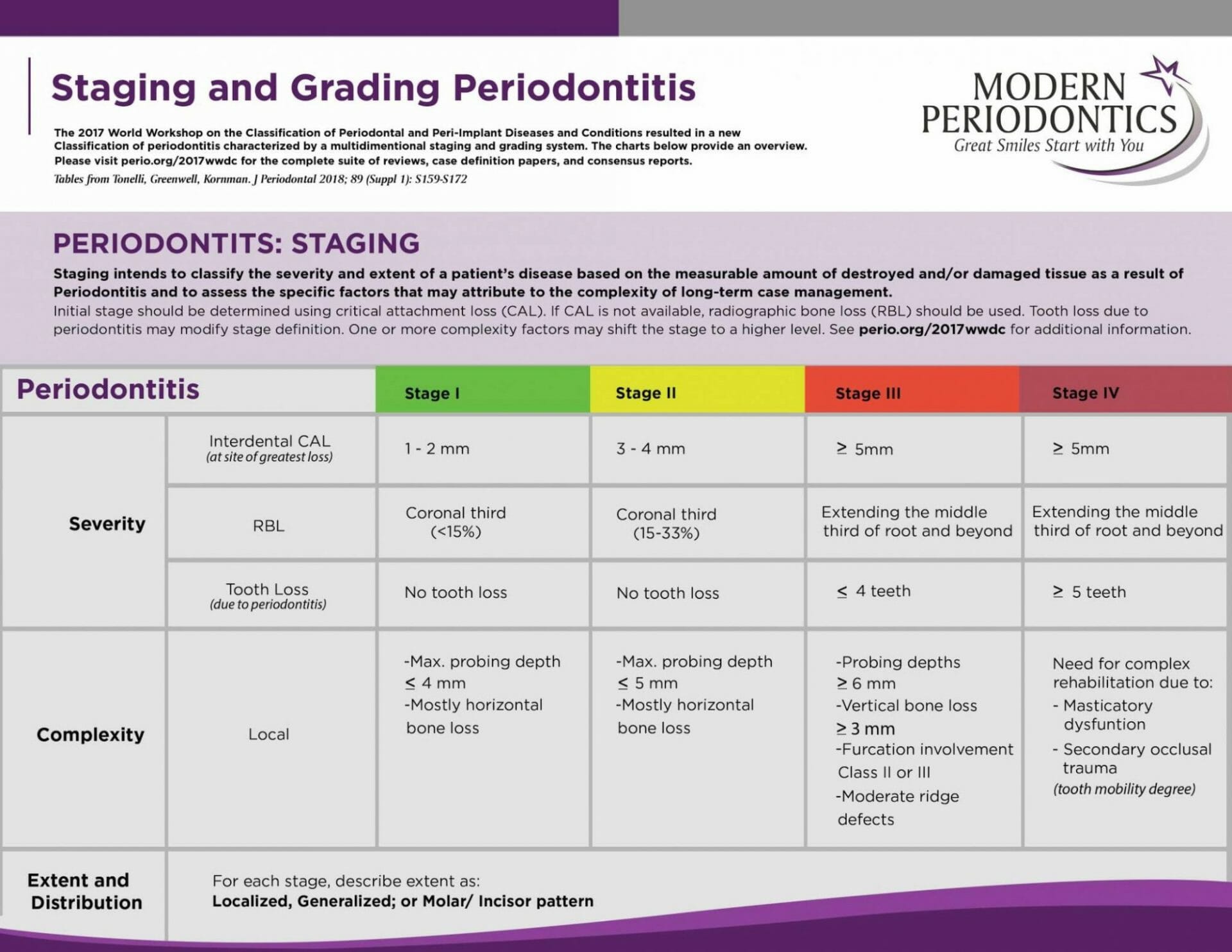
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis What You Need to Know Delta Dental
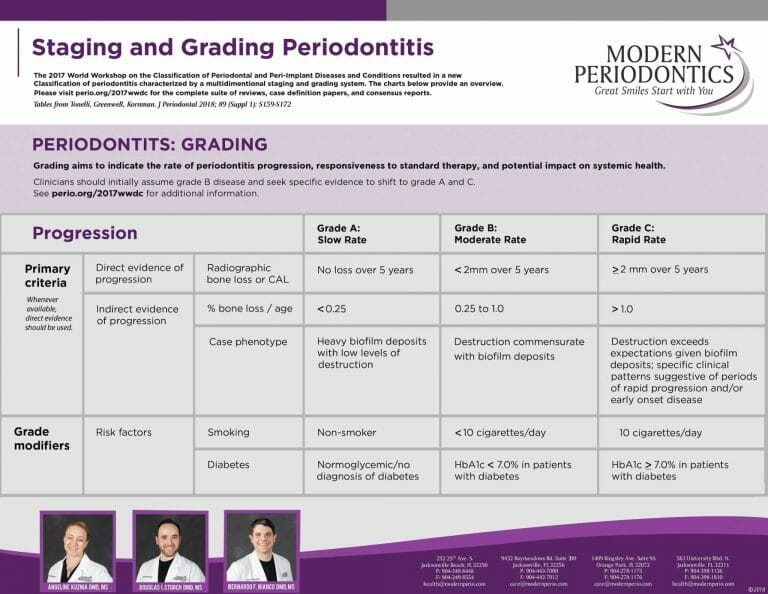
Staging and Grading Periodontitis
Strategies for Periodontal Risk Assessment and Prognosis Decisions in Dentistry
Determination of prognosis in periodontics
Periodontal (Gum) Diseases, Such As Gingivitis And Periodontitis, Are Largely Preventable And Treatable.
Periodontitis (Gum Disease) Occurs When The Gums Become Infected And Inflamed Due To A Buildup Of Plaque And Tartar On The Teeth.
The Goal Of Periodontal Treatment Is To Eliminate Dysbiotic Plaque Biofilm From The Tooth Surface And To Establish An Environment That Allows The Maintenance Of Health.
Related Post: