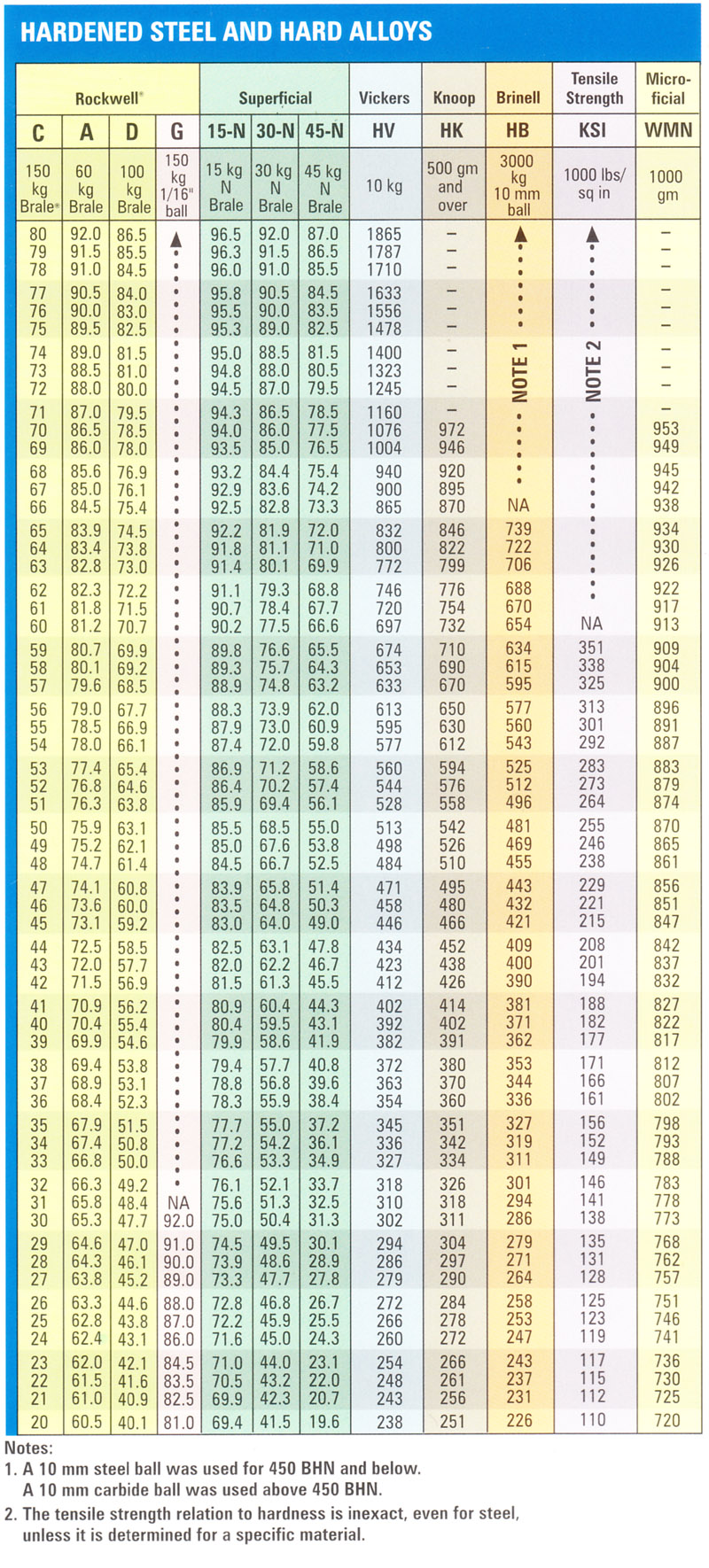
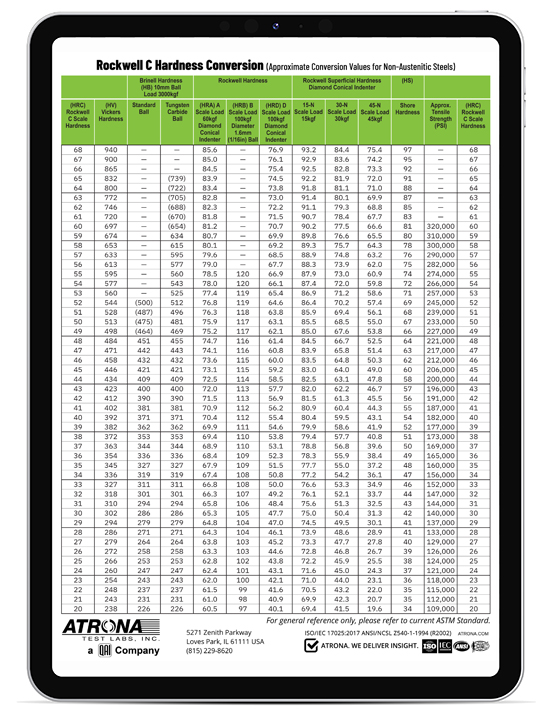
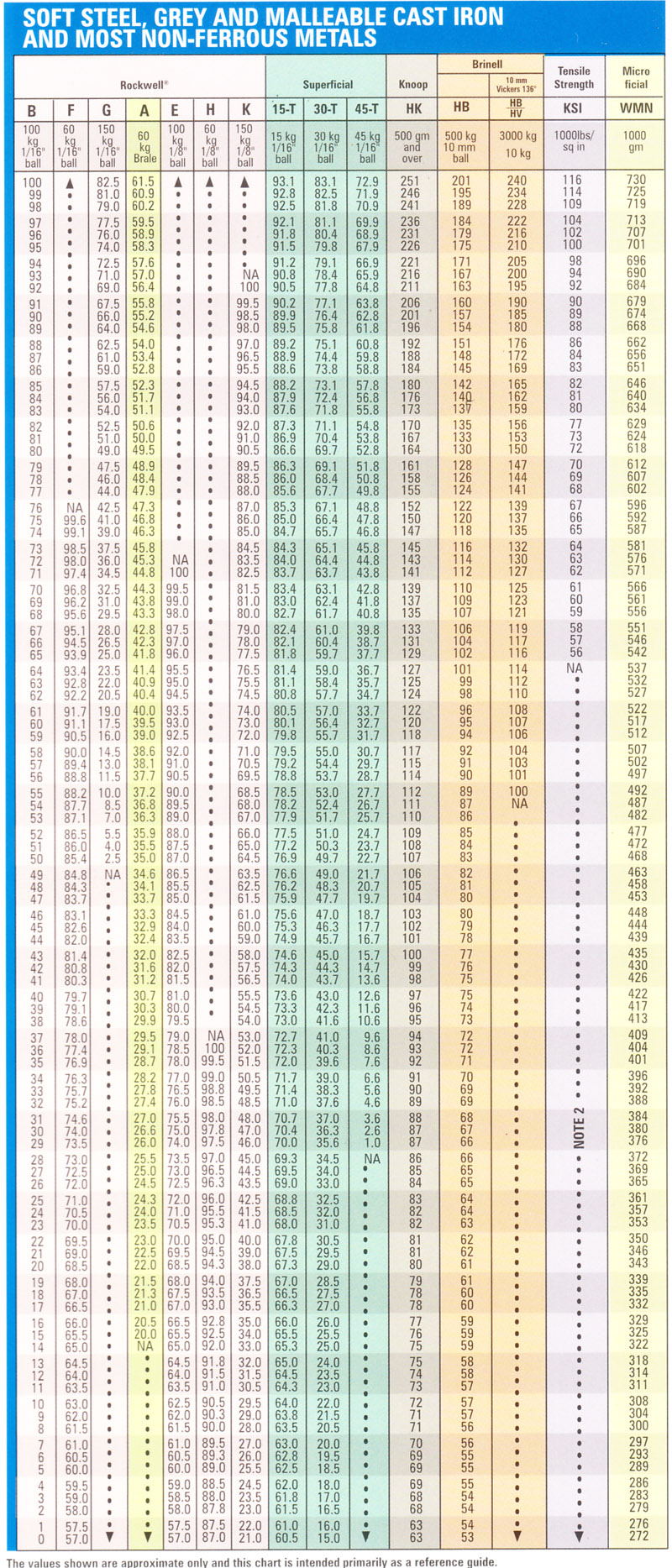
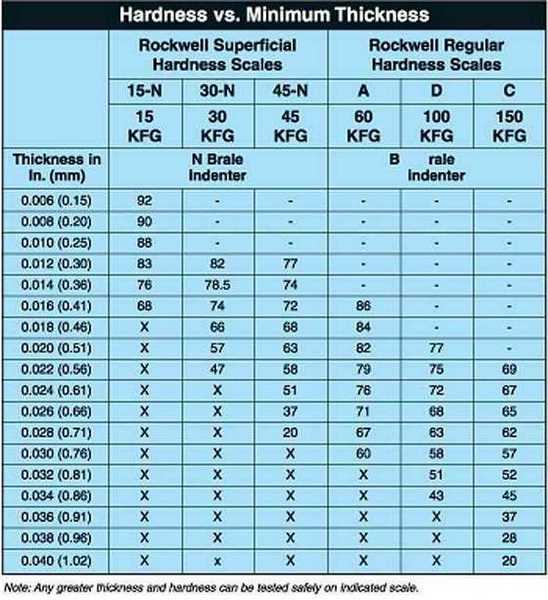
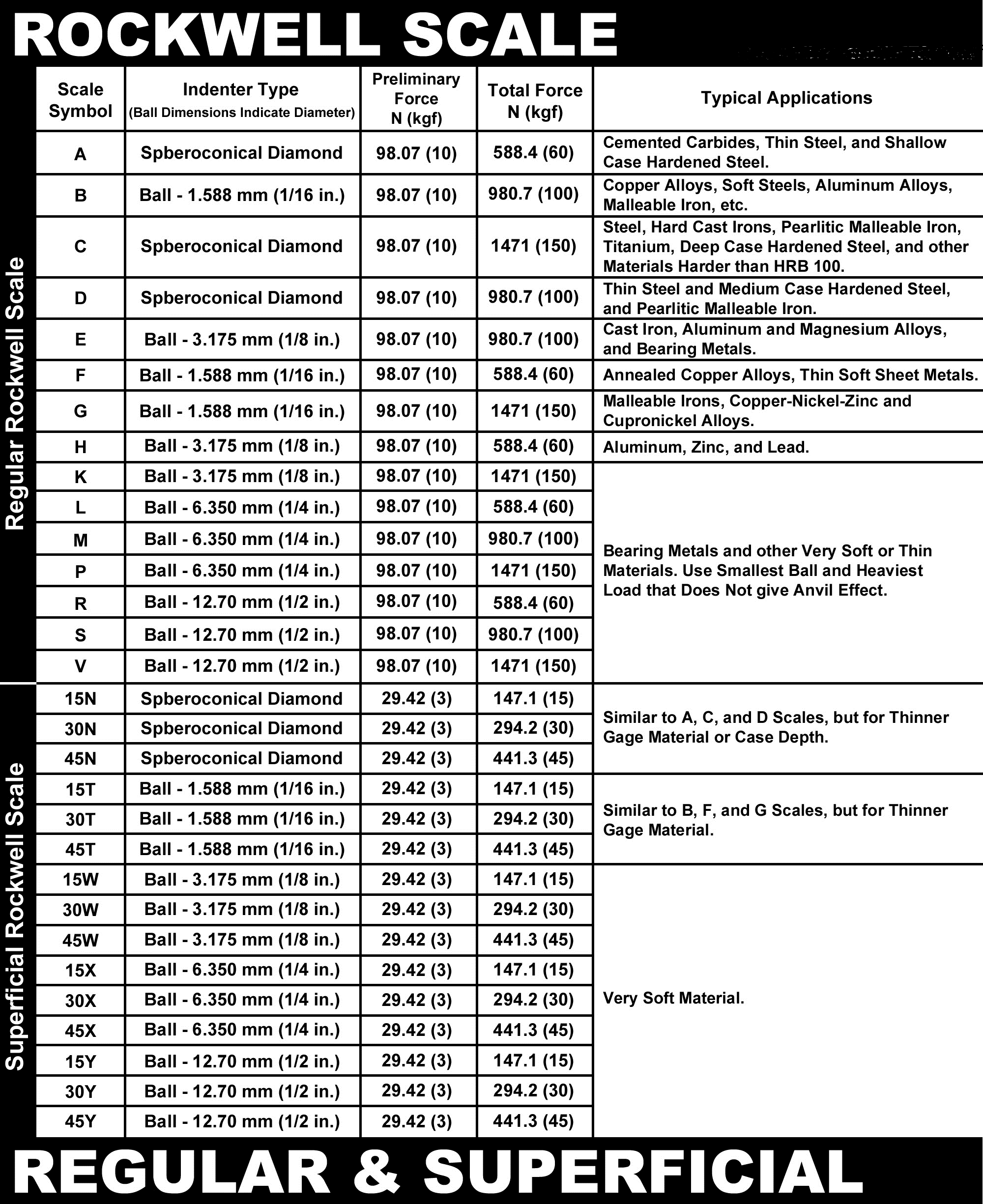
Rockwell Scale Chart
Rockwell Scale Chart - Less accurate for cold worked condition and for austenitic steels. N and s = various scale factors that can be found in the chart below. Hardness conversion chart with standards including brinell, rockwell b scale, rockwell c scale, vickers and others. This table shows approximate hardness of steel using brinell, rockwell b and c and vickers scales. D=depth from zero load point. The equation for rockwell hardness is , where d is the depth in mm (from the zero load point), and n and h are scale factors that depend on the scale of the test being used (see following. These conversion charts are provided for guidance only as each scales uses different. This hardness conversion table lets you easily compare values across the most widely used hardness scales, including rockwell, vickers, brinell, knoop, and leeb as well as approximate. The equation for the rockwell hardness test for metals is below: Astm e18 contains a listing of all regular rockwell scales and typical materials for which these scales are applicable. The equation for rockwell hardness is , where d is the depth in mm (from the zero load point), and n and h are scale factors that depend on the scale of the test being used (see following. Hardness conversion chart with standards including brinell, rockwell b scale, rockwell c scale, vickers and others. The equation for the rockwell hardness test for metals is below: D=depth from zero load point. The table below converts brinell hardness to rockwell hardness scales and vice versa, then compares those to the approximate tensile strength that those scales indicate. This hardness conversion table lets you easily compare values across the most widely used hardness scales, including rockwell, vickers, brinell, knoop, and leeb as well as approximate. Less accurate for cold worked condition and for austenitic steels. This table shows approximate hardness of steel using brinell, rockwell b and c and vickers scales. Astm e18 contains a listing of all regular rockwell scales and typical materials for which these scales are applicable. These conversion charts are provided for guidance only as each scales uses different. Use these tables in selecting the scale that is appropriate for your. Hardness conversion chart with standards including brinell, rockwell b scale, rockwell c scale, vickers and others. The table below converts brinell hardness to rockwell hardness scales and vice versa, then compares those to the approximate tensile strength that those scales indicate. Less accurate for cold worked condition and. This hardness conversion table lets you easily compare values across the most widely used hardness scales, including rockwell, vickers, brinell, knoop, and leeb as well as approximate. Use these tables in selecting the scale that is appropriate for your. These conversion tables presents data in the rockwell a, b, c, d, e and f hardness range on the relationship among. The equation for the rockwell hardness test for metals is below: The table below converts brinell hardness to rockwell hardness scales and vice versa, then compares those to the approximate tensile strength that those scales indicate. These conversion tables presents data in the rockwell a, b, c, d, e and f hardness range on the relationship among brinell hardness, vickers. Hardness conversion chart with standards including brinell, rockwell b scale, rockwell c scale, vickers and others. Use these tables in selecting the scale that is appropriate for your. Less accurate for cold worked condition and for austenitic steels. The equation for rockwell hardness is , where d is the depth in mm (from the zero load point), and n and. D=depth from zero load point. The equation for rockwell hardness is , where d is the depth in mm (from the zero load point), and n and h are scale factors that depend on the scale of the test being used (see following. The table below converts brinell hardness to rockwell hardness scales and vice versa, then compares those to. These conversion charts are provided for guidance only as each scales uses different. Astm e18 contains a listing of all regular rockwell scales and typical materials for which these scales are applicable. N and s = various scale factors that can be found in the chart below. This table shows approximate hardness of steel using brinell, rockwell b and c. N and s = various scale factors that can be found in the chart below. The table below converts brinell hardness to rockwell hardness scales and vice versa, then compares those to the approximate tensile strength that those scales indicate. Hardness conversion chart with standards including brinell, rockwell b scale, rockwell c scale, vickers and others. This table shows approximate. Astm e18 contains a listing of all regular rockwell scales and typical materials for which these scales are applicable. Use these tables in selecting the scale that is appropriate for your. Hardness conversion chart with standards including brinell, rockwell b scale, rockwell c scale, vickers and others. These conversion tables presents data in the rockwell a, b, c, d, e. Use these tables in selecting the scale that is appropriate for your. D=depth from zero load point. This hardness conversion table lets you easily compare values across the most widely used hardness scales, including rockwell, vickers, brinell, knoop, and leeb as well as approximate. Less accurate for cold worked condition and for austenitic steels. These conversion tables presents data in. The equation for rockwell hardness is , where d is the depth in mm (from the zero load point), and n and h are scale factors that depend on the scale of the test being used (see following. These conversion charts are provided for guidance only as each scales uses different. Astm e18 contains a listing of all regular rockwell. The table below converts brinell hardness to rockwell hardness scales and vice versa, then compares those to the approximate tensile strength that those scales indicate. N and s = various scale factors that can be found in the chart below. Less accurate for cold worked condition and for austenitic steels. Astm e18 contains a listing of all regular rockwell scales and typical materials for which these scales are applicable. The equation for rockwell hardness is , where d is the depth in mm (from the zero load point), and n and h are scale factors that depend on the scale of the test being used (see following. These conversion charts are provided for guidance only as each scales uses different. D=depth from zero load point. This table shows approximate hardness of steel using brinell, rockwell b and c and vickers scales. The equation for the rockwell hardness test for metals is below: Use these tables in selecting the scale that is appropriate for your.Hardness Conversion Chart Rockwell "C" Hardness Range
Rockwell C Hardness Conversion Chart PDF ATRONA Test Labs Loves Park, Illinois
What is the Rockwell Scale? Hardness Tester
Hardness Conversion Chart Rockwell "B" Hardness Range
Rockwell C Hardness Scale Chart at Irene Troyer blog
Hardness Conversion Chart Rockwell Rockwell Hardness Scale C
Rockwell Hardness Scale Metals Chart
Rockwell Hardness C Scale Chart at Sandra Madrigal blog
Rockwell C Hardness Scale Chart at Irene Troyer blog
Rockwell Hardness Scale Indentor Load Chart
Hardness Conversion Chart With Standards Including Brinell, Rockwell B Scale, Rockwell C Scale, Vickers And Others.
This Hardness Conversion Table Lets You Easily Compare Values Across The Most Widely Used Hardness Scales, Including Rockwell, Vickers, Brinell, Knoop, And Leeb As Well As Approximate.
These Conversion Tables Presents Data In The Rockwell A, B, C, D, E And F Hardness Range On The Relationship Among Brinell Hardness, Vickers Hardness, Rockwell Superficial, Hardness,.
Related Post: