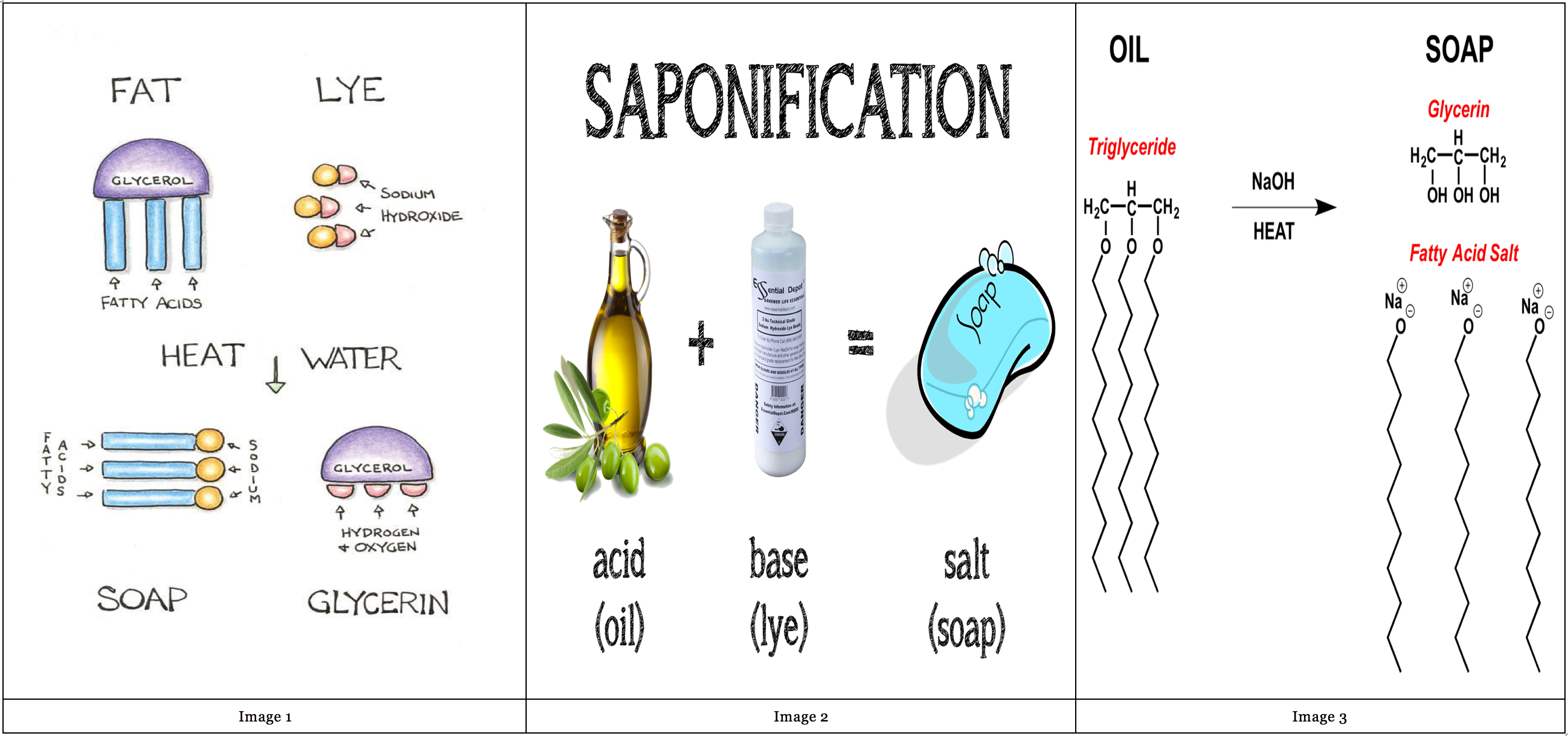
Saponification Chart
Saponification Chart - This process involves hydrolysis, where water molecules. Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into carboxylate salts and alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali. This process is called basic hydrolysis of esters. Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester to form an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid in acidic or essential conditions. When esters are treated with hydroxide ion, followed by neutralization with acid, they are converted into carboxylic acids. Saponification is the reaction where an ester is hydrolyzed into an alcohol and a carboxylic acid salt upon the addition of an aqueous base. Saponification is the fundamental chemical reaction in soap making where triglycerides from fats or oils react with a strong alkali, typically sodium hydroxide or potassium. The reaction is called a saponification from the latin sapo which means soap. Typically aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions are used. Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction with water and a base. Typically aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions are used. Saponification is the fundamental chemical reaction in soap making where triglycerides from fats or oils react with a strong alkali, typically sodium hydroxide or potassium. This process involves hydrolysis, where water molecules. Saponification is a chemical process in which triglycerides undergo an interaction with lye made from sodium or potassium hydroxide resulting in glycerol as well as a fatty acid. Saponification is a process by which triglycerides are reacted with sodium or potassium hydroxide (lye) to produce glycerol and a fatty acid salt called soap. Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction with water and a base. Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into carboxylate salts and alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali. In this article, we will explain the saponification. The alkali used in this process is sodium hydroxide. Saponification is the reaction where an ester is hydrolyzed into an alcohol and a carboxylic acid salt upon the addition of an aqueous base. This process involves hydrolysis, where water molecules. Saponification is a chemical process in which triglycerides undergo an interaction with lye made from sodium or potassium hydroxide resulting in glycerol as well as a fatty acid. In this article, we will explain the saponification. Saponification is the reaction where an ester is hydrolyzed into an alcohol and a carboxylic acid salt. Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction with water and a base. When esters are treated with hydroxide ion, followed by neutralization with acid, they are converted into carboxylic acids. Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester to form an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid in acidic or essential conditions.. Saponification is the fundamental chemical reaction in soap making where triglycerides from fats or oils react with a strong alkali, typically sodium hydroxide or potassium. Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester to form an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid in acidic or essential conditions. Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into carboxylate salts and alcohols. Saponification is a chemical process in which triglycerides undergo an interaction with lye made from sodium or potassium hydroxide resulting in glycerol as well as a fatty acid. Saponification is a chemical reaction between a strong base and a triglyceride that results in the formation of a salt. Saponification is a process by which triglycerides are reacted with sodium or. Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction with water and a base. Saponification is a chemical process in which triglycerides undergo an interaction with lye made from sodium or potassium hydroxide resulting in glycerol as well as a fatty acid. When esters are treated with hydroxide ion, followed by neutralization with acid, they. Saponification is the fundamental chemical reaction in soap making where triglycerides from fats or oils react with a strong alkali, typically sodium hydroxide or potassium. In this article, we will explain the saponification. Saponification is the reaction where an ester is hydrolyzed into an alcohol and a carboxylic acid salt upon the addition of an aqueous base. Saponification is the. Saponification is a chemical reaction between a strong base and a triglyceride that results in the formation of a salt. This process is called basic hydrolysis of esters. Saponification is the reaction where an ester is hydrolyzed into an alcohol and a carboxylic acid salt upon the addition of an aqueous base. Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into. The reaction is called a saponification from the latin sapo which means soap. This process involves hydrolysis, where water molecules. Saponification is a chemical reaction between a strong base and a triglyceride that results in the formation of a salt. This process is called basic hydrolysis of esters. Saponification is the reaction where an ester is hydrolyzed into an alcohol. Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester to form an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid in acidic or essential conditions. In this article, we will explain the saponification. This process is called basic hydrolysis of esters. This process involves hydrolysis, where water molecules. Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction. This process involves hydrolysis, where water molecules. Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction with water and a base. Typically aqueous sodium hydroxide solutions are used. Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester to form an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid in acidic or essential conditions. Saponification is a chemical. Saponification is the hydrolysis of an ester to form an alcohol and the salt of a carboxylic acid in acidic or essential conditions. The alkali used in this process is sodium hydroxide. Saponification is a chemical process in which triglycerides undergo an interaction with lye made from sodium or potassium hydroxide resulting in glycerol as well as a fatty acid. Saponification is the fundamental chemical reaction in soap making where triglycerides from fats or oils react with a strong alkali, typically sodium hydroxide or potassium. This process involves hydrolysis, where water molecules. Saponification is a chemical reaction between a strong base and a triglyceride that results in the formation of a salt. Esters can be cleaved back into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol by reaction with water and a base. The reaction is called a saponification from the latin sapo which means soap. In this article, we will explain the saponification. Saponification is a process by which triglycerides are reacted with sodium or potassium hydroxide (lye) to produce glycerol and a fatty acid salt called soap. When esters are treated with hydroxide ion, followed by neutralization with acid, they are converted into carboxylic acids. Saponification is a process of cleaving esters into carboxylate salts and alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali.Faire son savon soimême la saponification à froid Bioté Naturelle
Soap Saponification Charts & Information Natural Health
Average chain length and saponification values for common edible oils Download Scientific Diagram
Soap saponification charts information natural health Artofit
Soap Saponification Charts & Information Cold process soap recipes, Soap making recipes
أغسطس 2018 sciences
Soap saponification charts information natural health Artofit
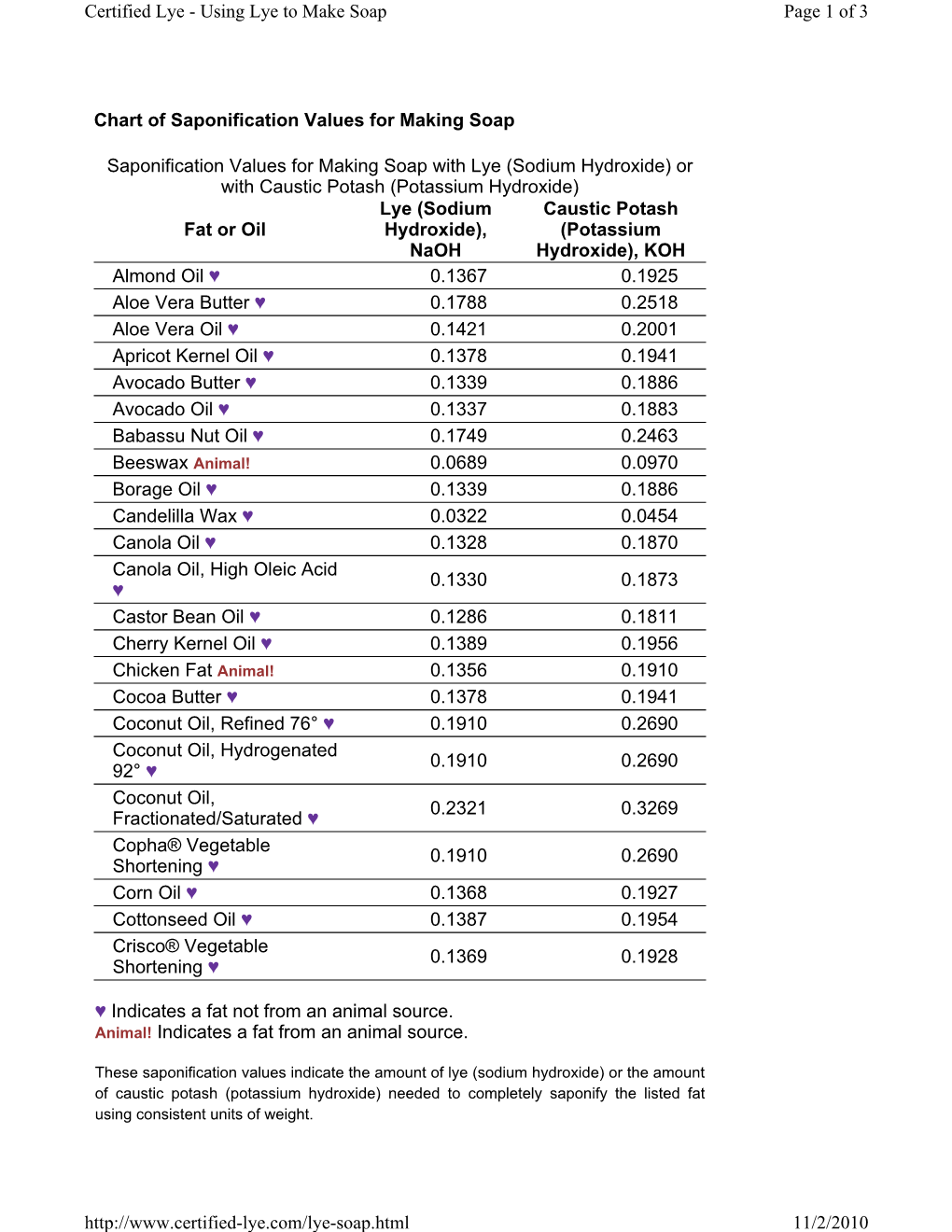
Chart of Saponification Values for Making Soap Fat Or Oil DocsLib
Helping Vocabulary to Stick 7 Successful Strategies for Schooling Saponification (or at least
Free fatty acid content, Saponification Value and Kinematic viscosity... Download Table
This Process Is Called Basic Hydrolysis Of Esters.
Saponification Is The Reaction Where An Ester Is Hydrolyzed Into An Alcohol And A Carboxylic Acid Salt Upon The Addition Of An Aqueous Base.
Typically Aqueous Sodium Hydroxide Solutions Are Used.
Related Post: