Slso Seating Chart
Slso Seating Chart - It’s commonly used practice to declare all project dependencies under implementation configuration. It is needed for testing the code. Tasks.named('jar') { from(sourcesets.test.output) } however, i have to wonder why you would want to do this? This works for me (in gradle 5.6). In project b, you just need to add a testcompile dependency: Similarly, the buildscript block allows us to declare. It will list the dependencies as available to your tests. Learn how to efficiently add dependencies to your gradle test classpath. Assuming you are using a gradle wrapper, you can use the following. What i need is a custom testing suit (integrationtest let’s say). Learn how to efficiently add dependencies to your gradle test classpath. Similarly, the buildscript block allows us to declare. You can add the compile test class files to the jar using: It will list the dependencies as available to your tests. In project b, you just need to add a testcompile dependency: This works for me (in gradle 5.6). As we saw before, we can declare the external dependencies of our source code and tests inside the dependencies block. Gradle needs specific information, called gav coordinates, to locate and download a dependency. I'm sure it can be achieved with proper. Tasks.named('jar') { from(sourcesets.test.output) } however, i have to wonder why you would want to do this? I'm sure it can be achieved with proper. Gav stands for group, artifact, and version — three pieces of information that. In project b, you just need to add a testcompile dependency: Assuming you are using a gradle wrapper, you can use the following. Learn how to efficiently add dependencies to your gradle test classpath. Tasks.named('jar') { from(sourcesets.test.output) } however, i have to wonder why you would want to do this? As we saw before, we can declare the external dependencies of our source code and tests inside the dependencies block. It’s commonly used practice to declare all project dependencies under implementation configuration. I'm sure it can be achieved with proper. Learn how to efficiently. Here, implementation is for dependencies that are required when. This works for me (in gradle 5.6). You can add the compile test class files to the jar using: It is needed for testing the code. I'm sure it can be achieved with proper. Assuming you are using a gradle wrapper, you can use the following. Tasks.named('jar') { from(sourcesets.test.output) } however, i have to wonder why you would want to do this? It will list the dependencies as available to your tests. Learn how to efficiently add dependencies to your gradle test classpath. What i need is a custom testing suit (integrationtest let’s say). It is needed for testing the code. In project b, you just need to add a testcompile dependency: Here, implementation is for dependencies that are required when. Similarly, the buildscript block allows us to declare. Gav stands for group, artifact, and version — three pieces of information that. I'm sure it can be achieved with proper. It’s commonly used practice to declare all project dependencies under implementation configuration. You can add the compile test class files to the jar using: Gav stands for group, artifact, and version — three pieces of information that. Assuming you are using a gradle wrapper, you can use the following. I'm sure it can be achieved with proper. It will list the dependencies as available to your tests. This works for me (in gradle 5.6). Here, implementation is for dependencies that are required when. Learn how to efficiently add dependencies to your gradle test classpath. Gav stands for group, artifact, and version — three pieces of information that. It is needed for testing the code. Here, implementation is for dependencies that are required when. Learn how to efficiently add dependencies to your gradle test classpath. This works for me (in gradle 5.6). Similarly, the buildscript block allows us to declare. You can add the compile test class files to the jar using: It’s commonly used practice to declare all project dependencies under implementation configuration. Gradle needs specific information, called gav coordinates, to locate and download a dependency. It will list the dependencies as available to your tests. Here, implementation is for dependencies that are required when. Gradle needs specific information, called gav coordinates, to locate and download a dependency. Gav stands for group, artifact, and version — three pieces of information that. Learn how to efficiently add dependencies to your gradle test classpath. I'm sure it can be achieved with proper. In project b, you just need to add a testcompile dependency: It is needed for testing the code. What i need is a custom testing suit (integrationtest let’s say). Tasks.named('jar') { from(sourcesets.test.output) } however, i have to wonder why you would want to do this? Gav stands for group, artifact, and version — three pieces of information that. Learn how to efficiently add dependencies to your gradle test classpath. Similarly, the buildscript block allows us to declare. It will list the dependencies as available to your tests. As we saw before, we can declare the external dependencies of our source code and tests inside the dependencies block. This works for me (in gradle 5.6). Gradle needs specific information, called gav coordinates, to locate and download a dependency. I'm sure it can be achieved with proper.Stl Symphony Seating Chart
Returning Subscriber Dallas Symphony Orchestra
St Louis Symphony Orchestra Seating Chart IUCN Water
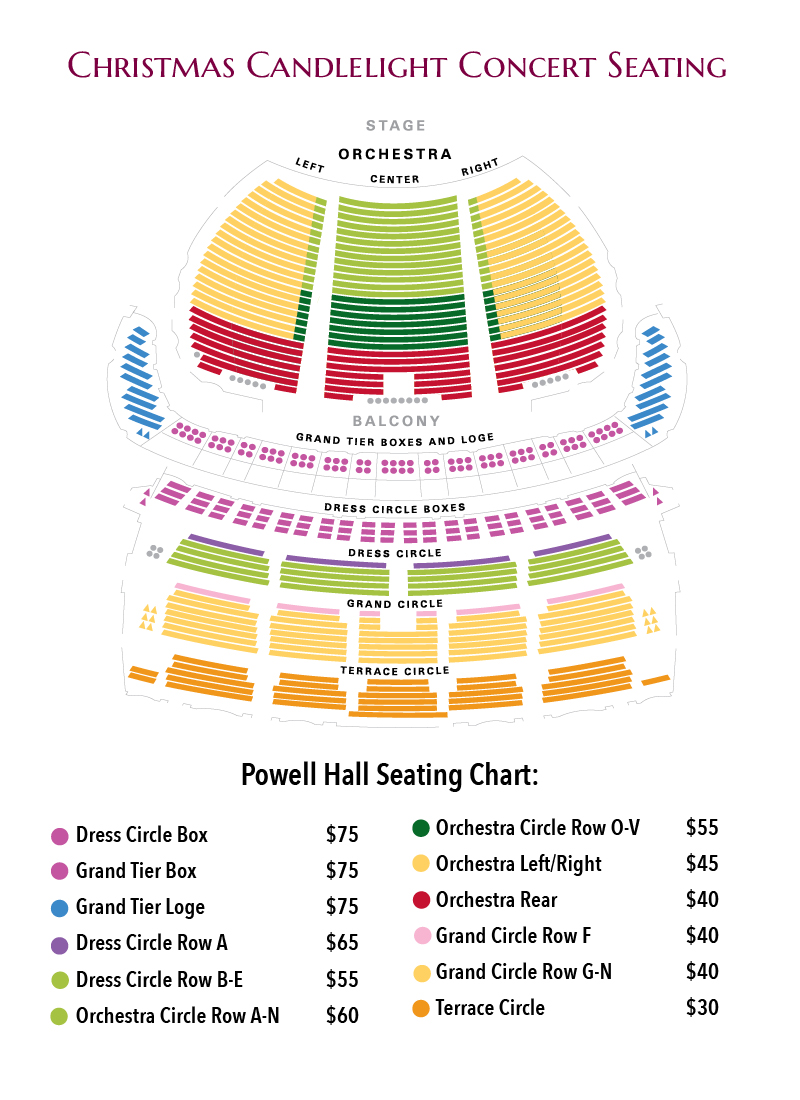
Powell Hall Seating Chart Powell Hall St. Louis, Missouri
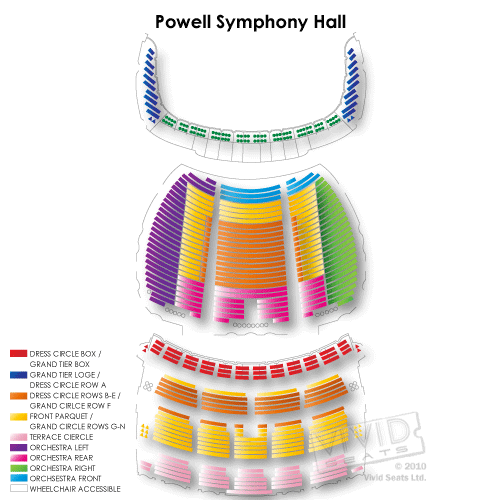
Powell Symphony St Louis IQS Executive
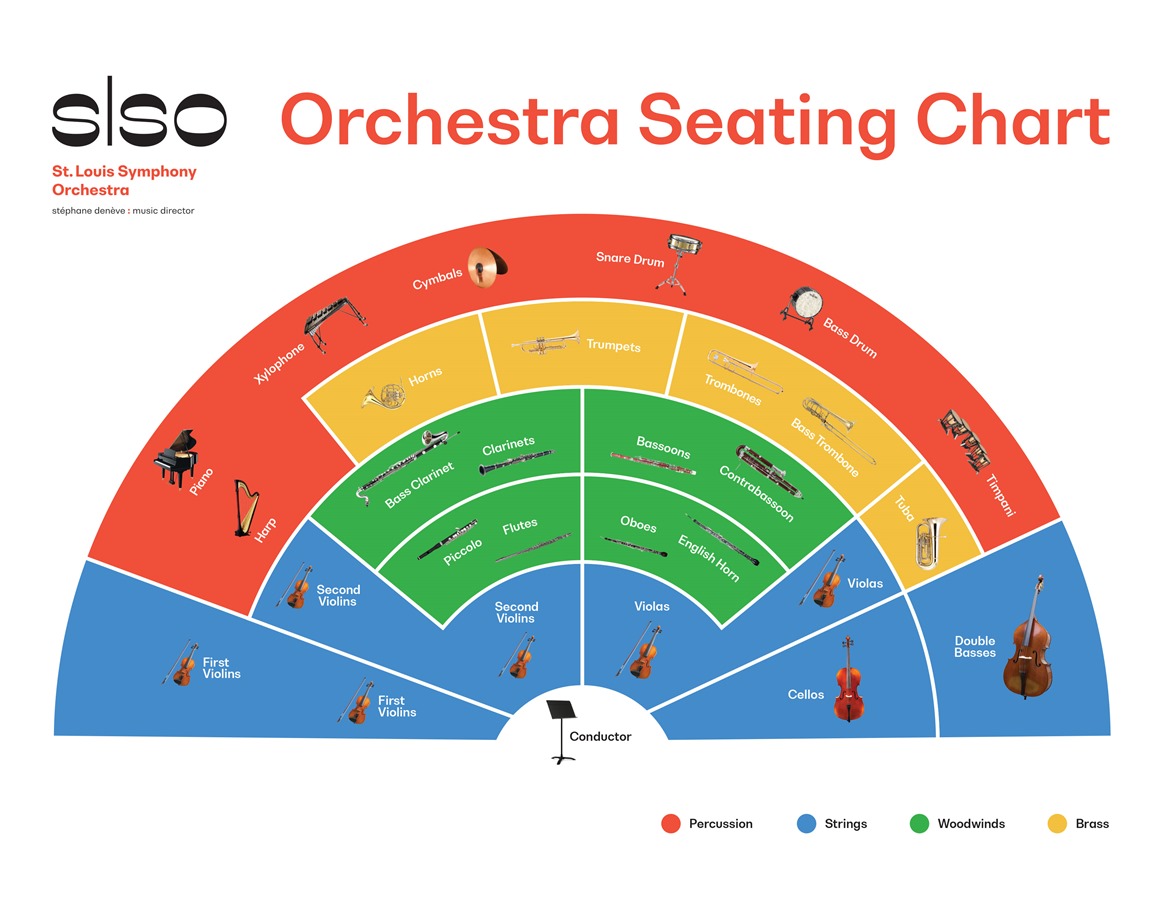
Orchestra Seating Chart Worksheet
stl symphony seating chart
Seating Charts Atlanta Symphony Orchestra
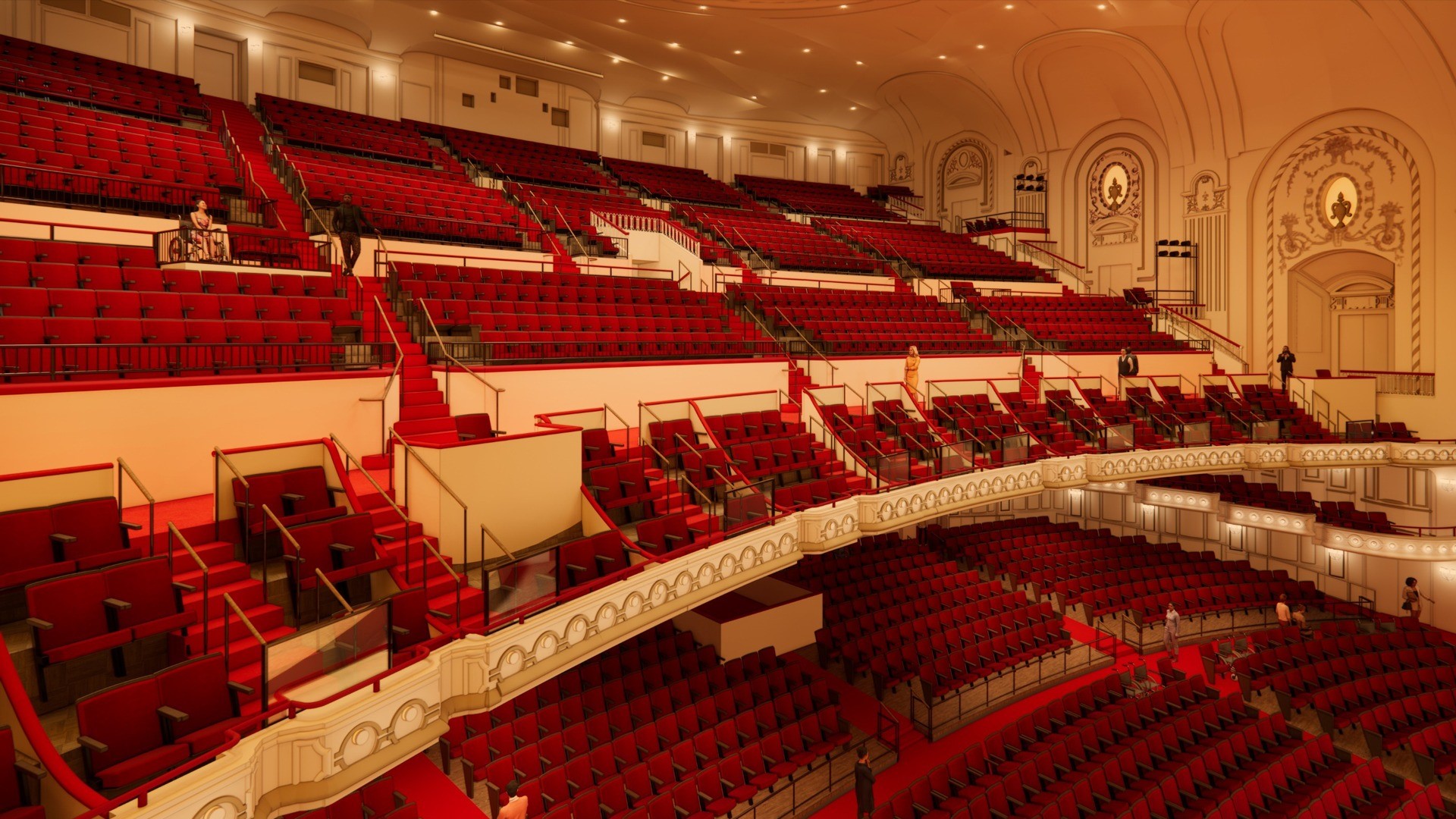
Take a look inside Powell Hall's 65,000foot expansion project
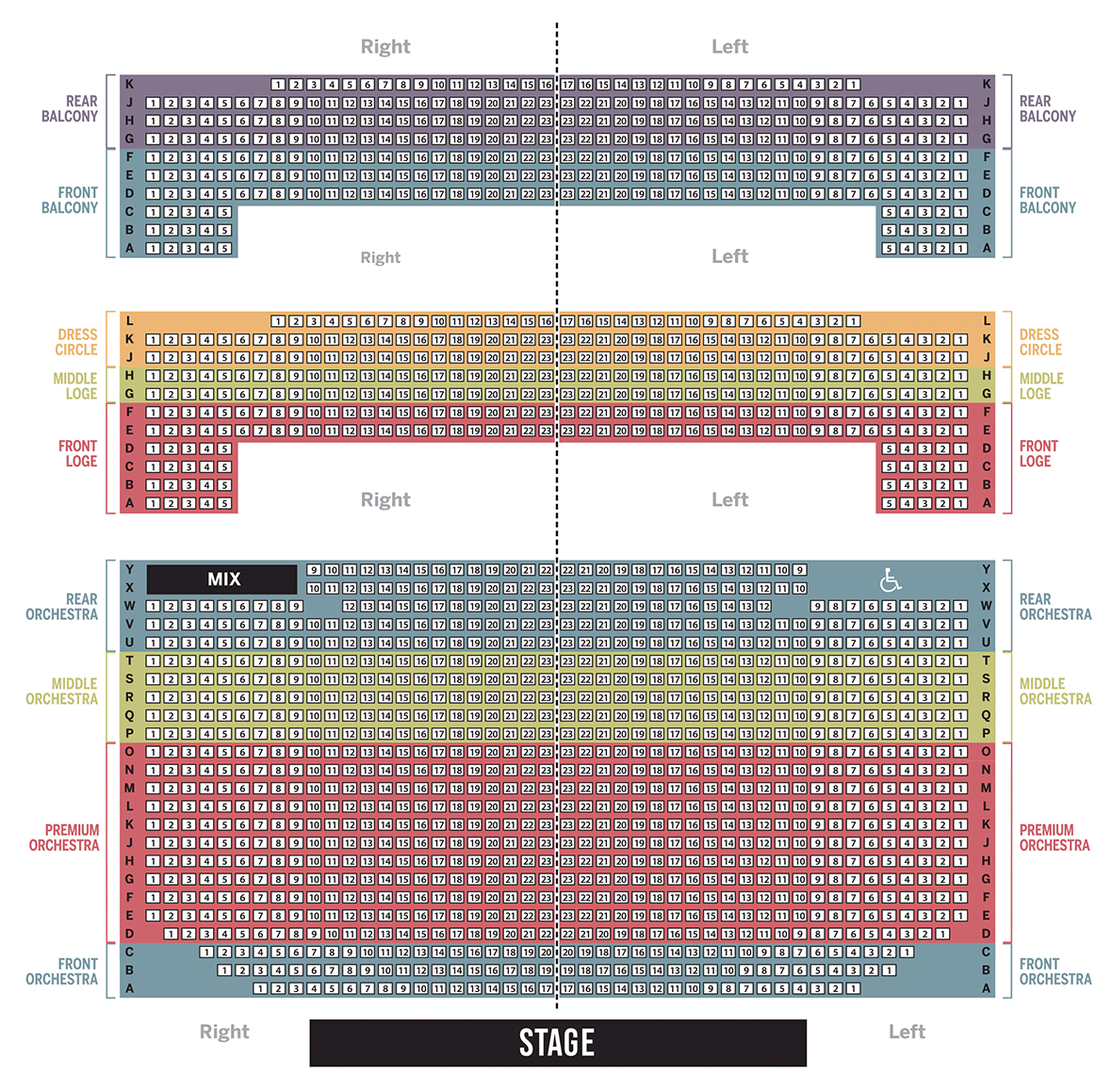
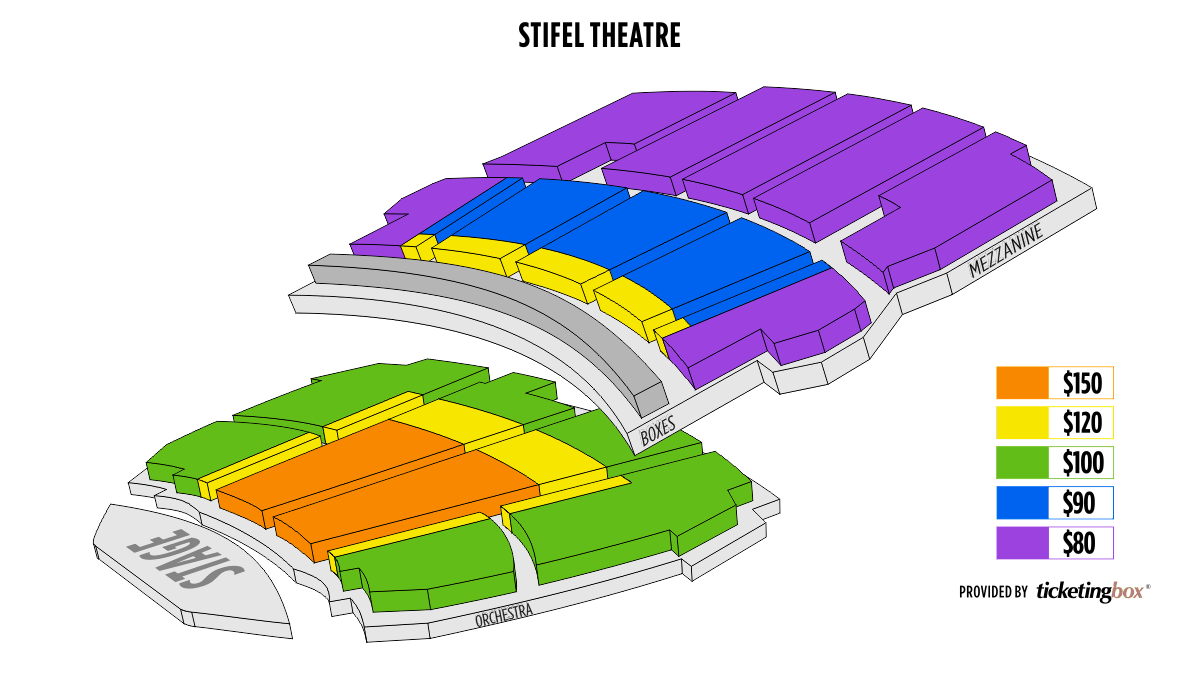
St. Louis Stifel Theatre (Formerly Peabody Opera House) Seating Chart
It’s Commonly Used Practice To Declare All Project Dependencies Under Implementation Configuration.
You Can Add The Compile Test Class Files To The Jar Using:
Assuming You Are Using A Gradle Wrapper, You Can Use The Following.
Here, Implementation Is For Dependencies That Are Required When.
Related Post: