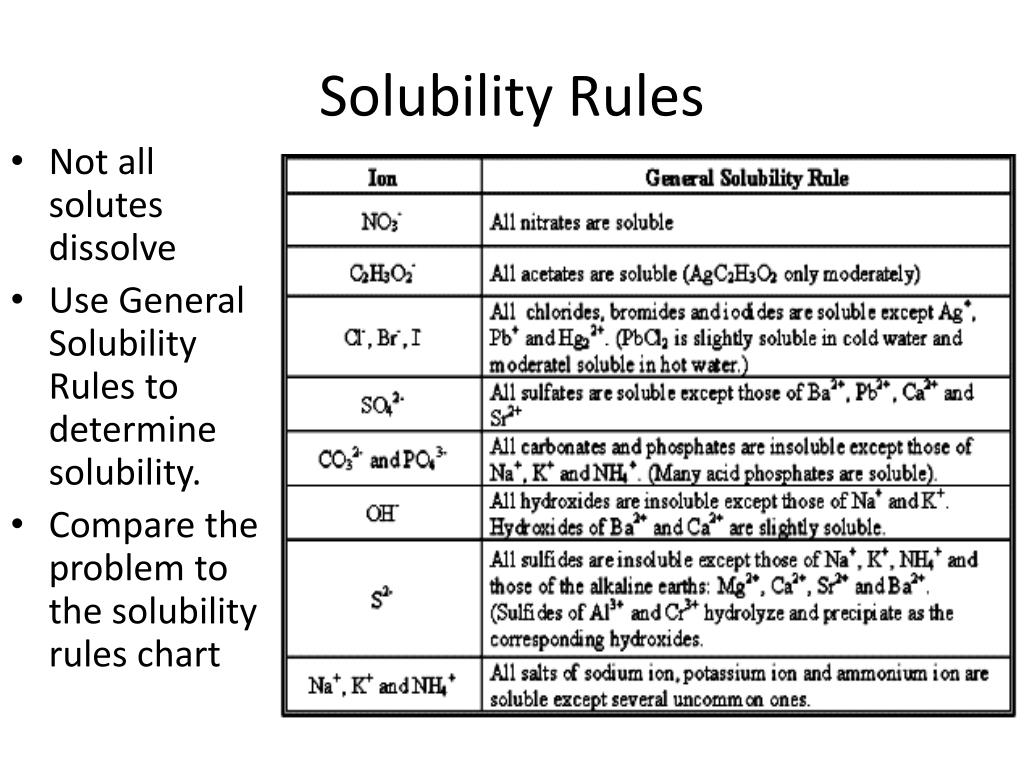
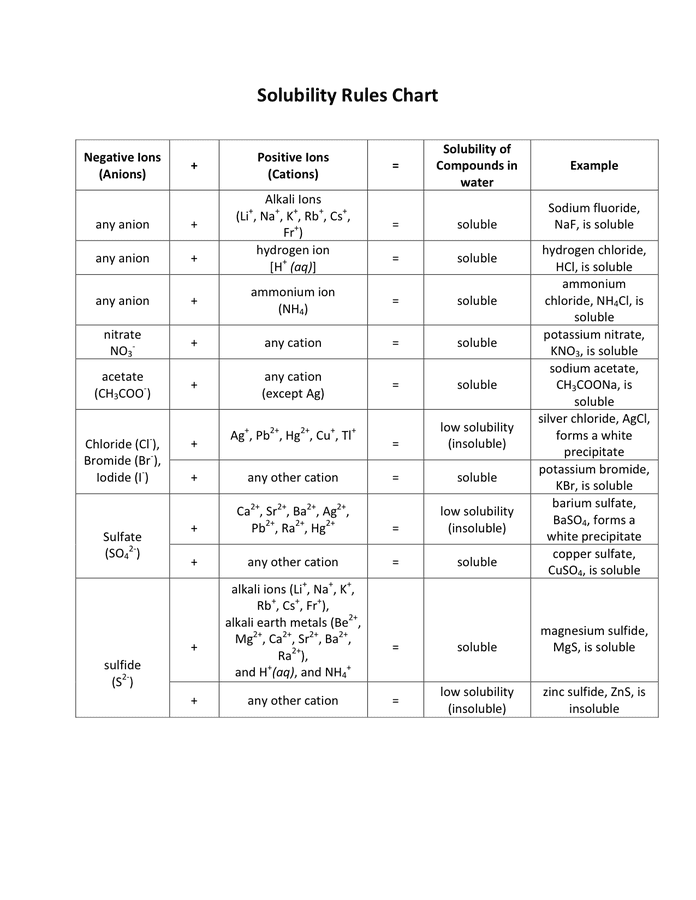
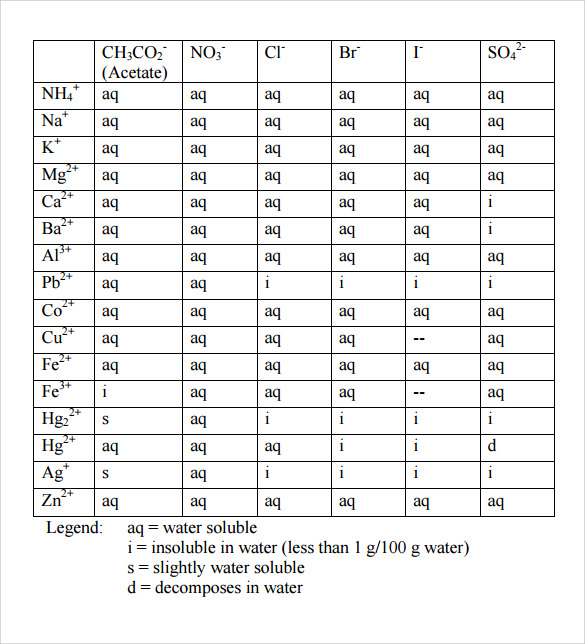
Solubility Rules Chart Chemistry
Solubility Rules Chart Chemistry - Solubility, degree to which a substance dissolves in a solvent to make a solution (usually expressed as grams of solute per litre of solvent). The concentration of salt in the solution at this point is known as its solubility. Solubility is defined as the upper limit of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at equilibrium. It is measured in terms of the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a. Solubility is the new bond formation between the solute molecules and solvent molecules. This is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a given. The process through which a solute in its solid, liquid, or. Solubility is the maximum concentration of a solute that can dissolve in a specific amount of a solvent at a given temperature. In such an equilibrium, le chatelier's principle can be used to explain most of. Solubility is a property referring to the ability for a given substance, the solute, to dissolve in a solvent. This is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a given. Solubility is how much of a substance can dissolve in another before the solution becomes saturated. There are a number of patterns in the data. The process through which a solute in its solid, liquid, or. Solubility, degree to which a substance dissolves in a solvent to make a solution (usually expressed as grams of solute per litre of solvent). The amount of salt that must be added to a given volume of solvent to form a saturated solution is called the solubility of the salt. Solubility of one fluid (liquid or gas). Solubility is defined as the upper limit of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at equilibrium. It is measured in terms of the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form. In terms of quantity, solubility is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known. Solubility is a property referring to the ability for a given substance, the solute, to dissolve in a solvent. It is measured in terms of the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a. Solubility of one fluid (liquid or gas). The process through which. Solubility of one fluid (liquid or gas). The solubility of a solute in a particular solvent is the maximum concentration that may be achieved under given. The process through which a solute in its solid, liquid, or. Solubility is how much of a substance can dissolve in another before the solution becomes saturated. In chemistry, solubility is the ability of. The concentration of salt in the solution at this point is known as its solubility. Solubility, degree to which a substance dissolves in a solvent to make a solution (usually expressed as grams of solute per litre of solvent). This is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a given. Solubility is defined. Solubility of one fluid (liquid or gas). In terms of quantity, solubility is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known. Solubility is how much of a substance can dissolve in another before the solution becomes saturated. Solubility is a property referring to the ability for a given substance, the solute, to dissolve in a solvent. There are. Solubility is the maximum concentration of a solute that can dissolve in a specific amount of a solvent at a given temperature. Solubility forms new bonds between solute molecules and solvent molecules. Solubility is the new bond formation between the solute molecules and solvent molecules. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form. Solubility is defined. Solubility of one fluid (liquid or gas). Solubility is the new bond formation between the solute molecules and solvent molecules. This is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a given. Solubility is how much of a substance can dissolve in another before the solution becomes saturated. The concentration of salt in the. Solubility is how much of a substance can dissolve in another before the solution becomes saturated. It is measured in terms of the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a. Solubility is defined as the upper limit of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at equilibrium. Solubility can change with temperature, pressure, and other chemical.. The process through which a solute in its solid, liquid, or. Solubility is the maximum concentration of a solute that can dissolve in a specific amount of a solvent at a given temperature. Solubility of one fluid (liquid or gas). In such an equilibrium, le chatelier's principle can be used to explain most of. It is measured in terms of. In terms of quantity, solubility is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known. Solubility forms new bonds between solute molecules and solvent molecules. The process through which a solute in its solid, liquid, or. In such an equilibrium, le chatelier's principle can be used to explain most of. The concentration of salt in the solution at this. Solubility is the maximum concentration of a solute that can dissolve in a specific amount of a solvent at a given temperature. Solubility of one fluid (liquid or gas). In such an equilibrium, le chatelier's principle can be used to explain most of. This is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a. The amount of salt that must be added to a given volume of solvent to form a saturated solution is called the solubility of the salt. It is measured in terms of the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a. In such an equilibrium, le chatelier's principle can be used to explain most of. Solubility can change with temperature, pressure, and other chemical. In terms of quantity, solubility is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known. Solubility is the new bond formation between the solute molecules and solvent molecules. The solubility of a solute in a particular solvent is the maximum concentration that may be achieved under given. The concentration of salt in the solution at this point is known as its solubility. Solubility of one fluid (liquid or gas). Solubility is defined as the upper limit of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at equilibrium. There are a number of patterns in the data. Solubility is how much of a substance can dissolve in another before the solution becomes saturated. In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. This is the maximum concentration of solute that dissolves in a known concentration of solvent at a given. Solubility is a property referring to the ability for a given substance, the solute, to dissolve in a solvent. Solubility is the maximum concentration of a solute that can dissolve in a specific amount of a solvent at a given temperature.PPT Solubility Rules PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5256674
Solubility Rules Chart in Word and Pdf formats
Solubility Rules Abbreviated Chart Free Download
Chemistry Solubility Rules Free Images at vector clip art online, royalty free
Solubility Rules Chart Solubility chemistry rules chart reactions chemical charts compounds
Solubility Rules Chart and Memorization Tips
Solubility Chart
Solubility Rules Pathways to Chemistry
8+ Solubility Rules Chart Templates Sample Templates
Solubility Table
Solubility, Degree To Which A Substance Dissolves In A Solvent To Make A Solution (Usually Expressed As Grams Of Solute Per Litre Of Solvent).
The Process Through Which A Solute In Its Solid, Liquid, Or.
Insolubility Is The Opposite Property, The Inability Of The Solute To Form.
Solubility Forms New Bonds Between Solute Molecules And Solvent Molecules.
Related Post: