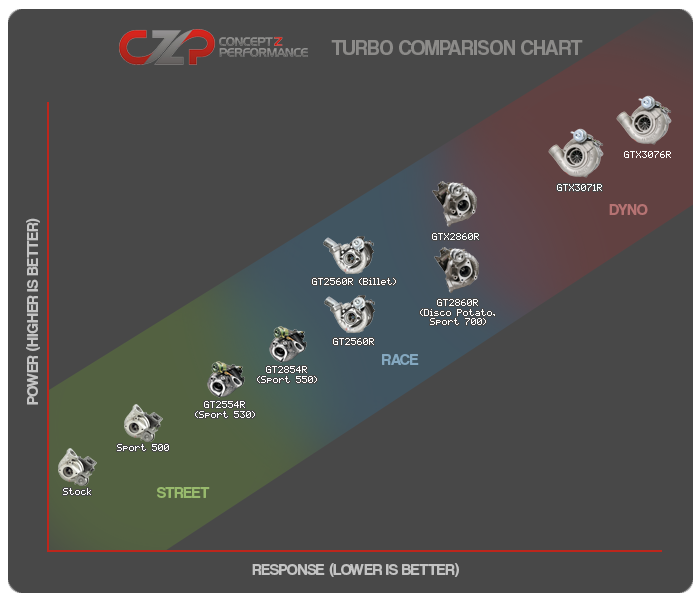
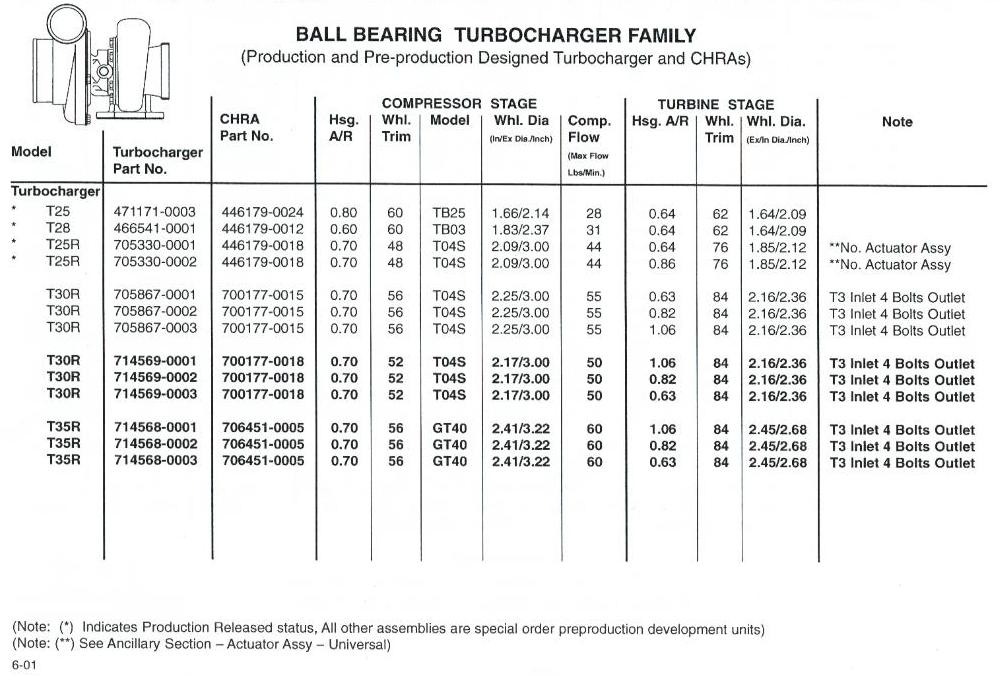
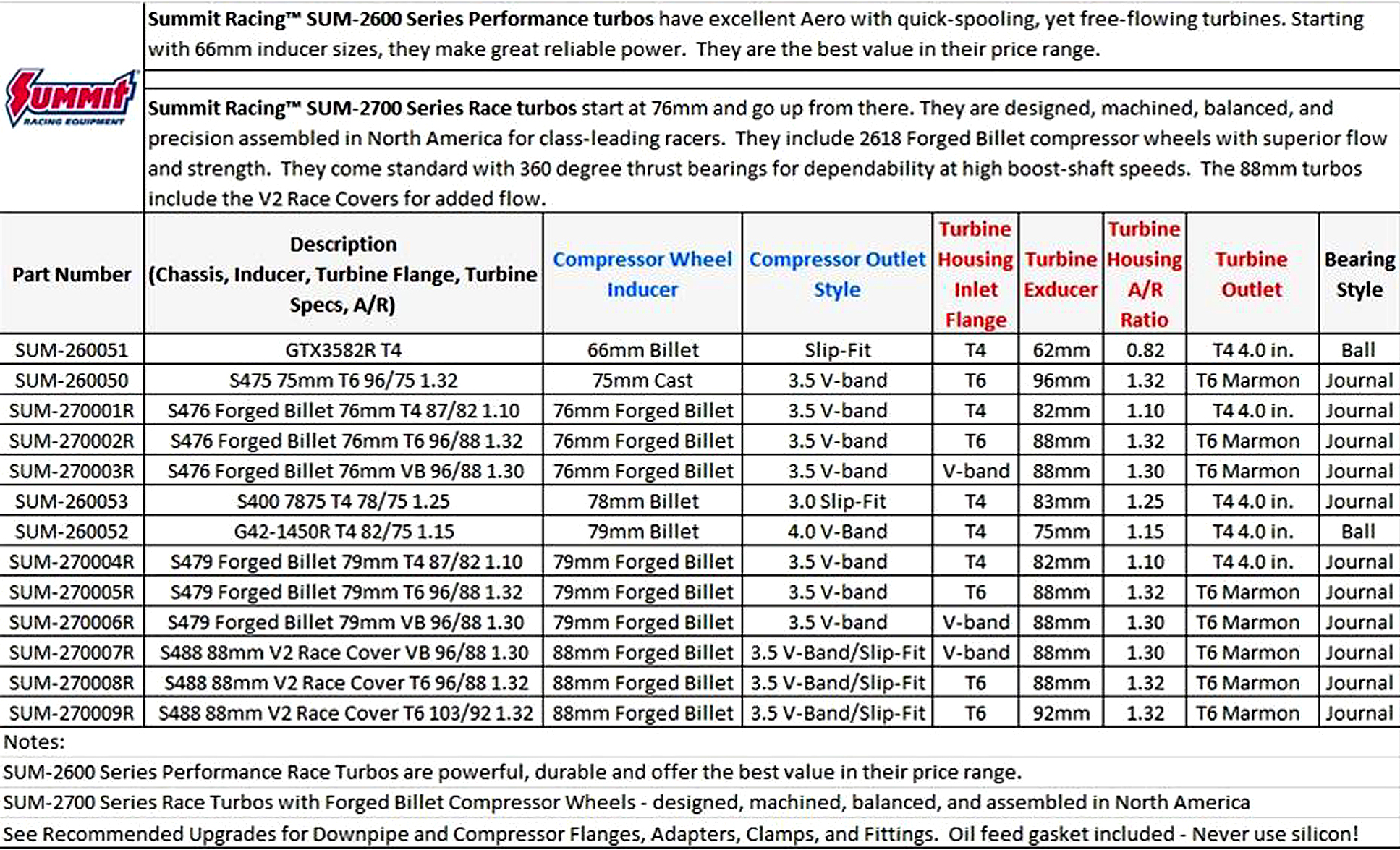
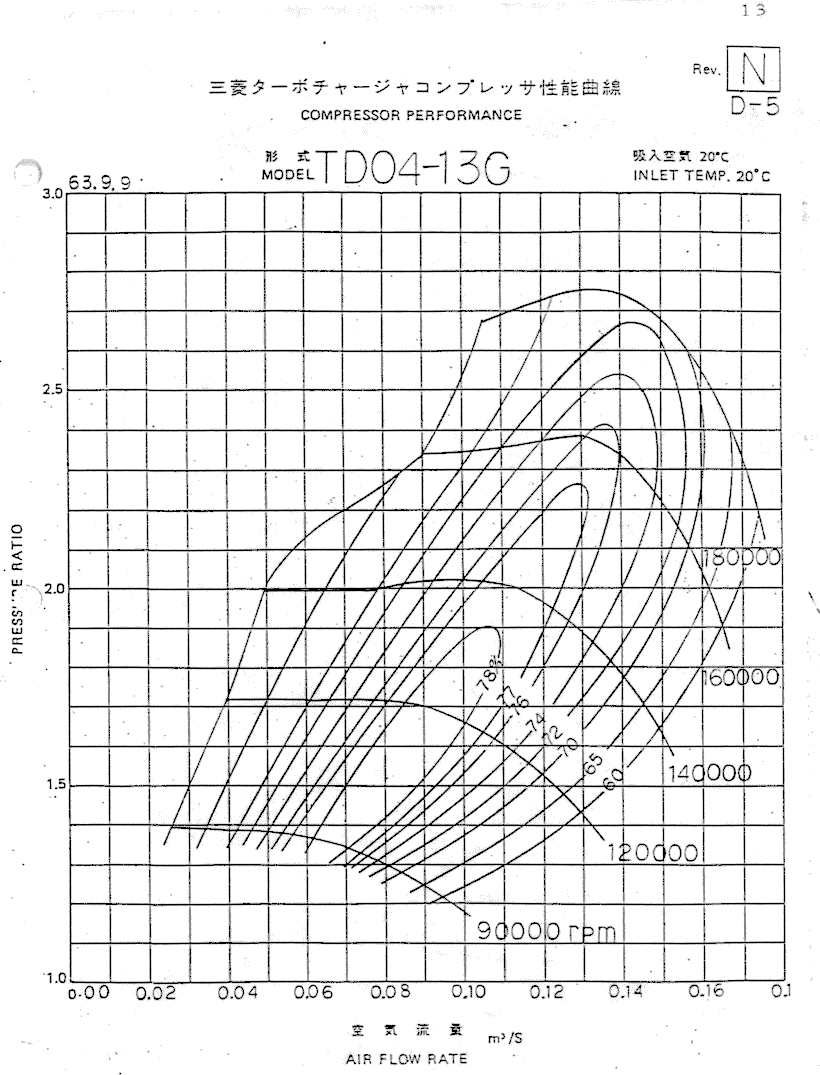
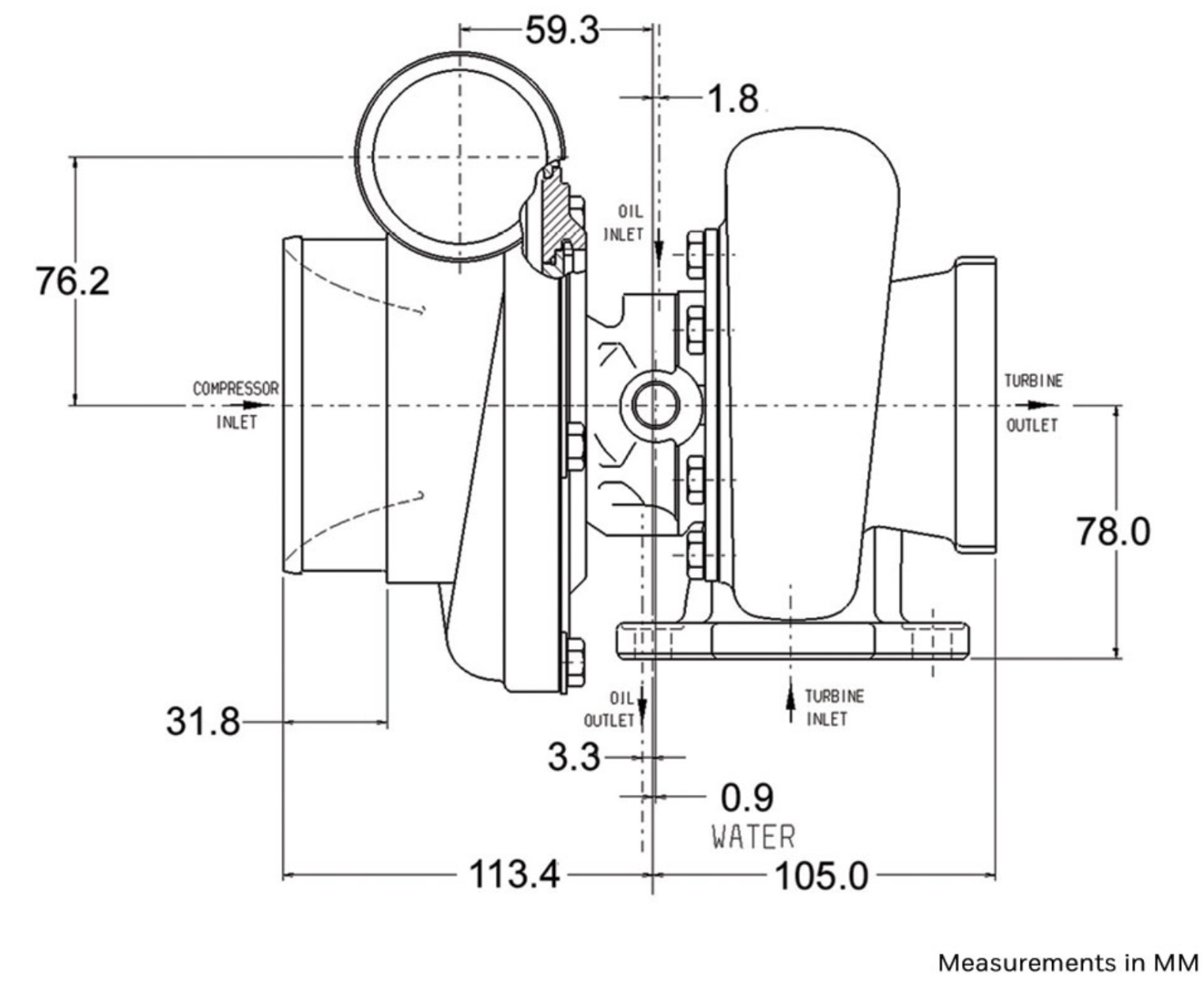
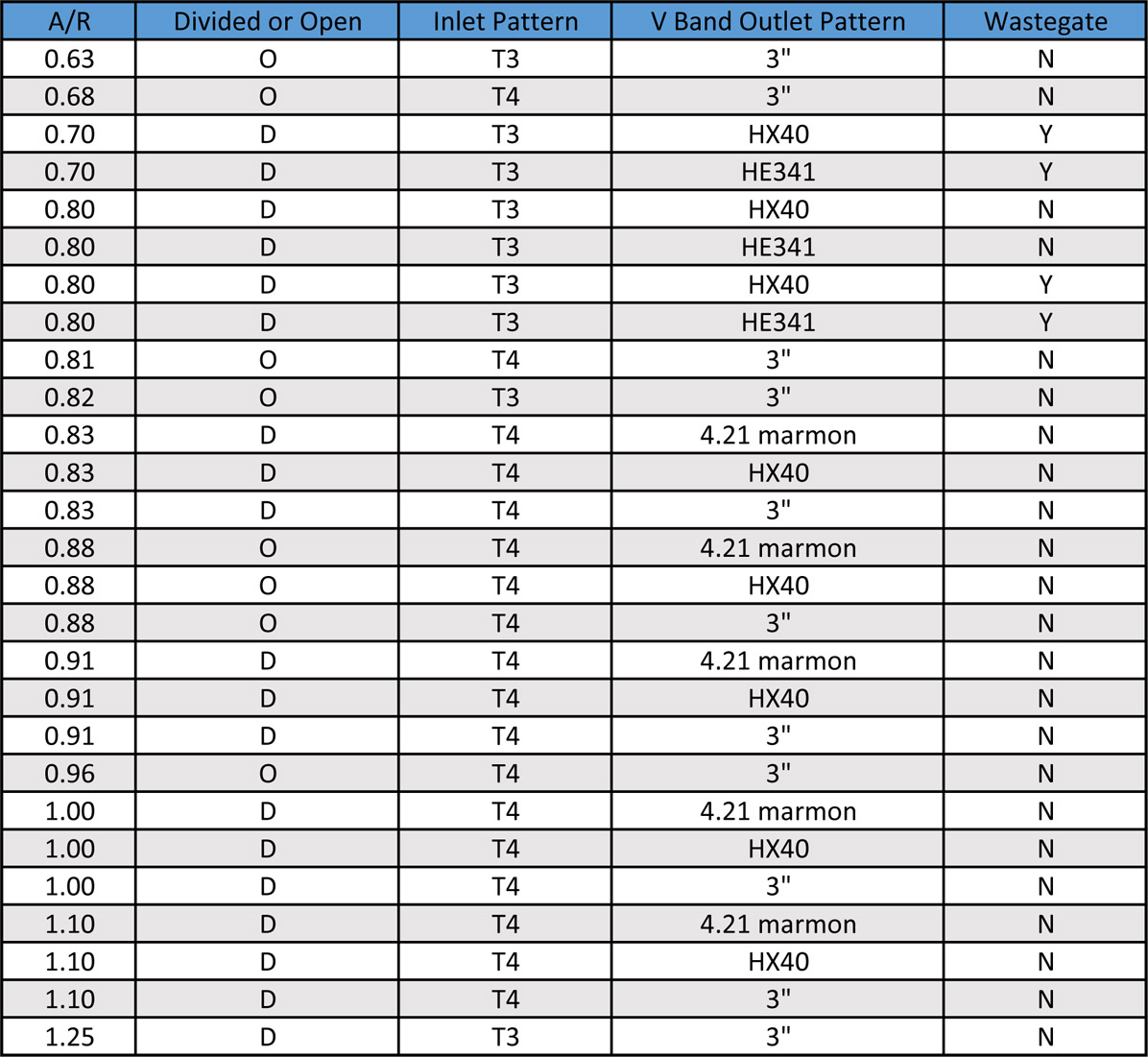
Turbocharger Size Chart
Turbocharger Size Chart - This increase in air means. A turbocharger, often called a turbo, is an integral component in modern ic engines. It enhances the performance and efficiency of ic engines by harnessing exhaust gases to compress. It does this without sacrificing fuel economy under conservative driving. This extra fuel is where. It is the job of the turbocharger to compress more air flowing into the engine’s cylinder. Learn how turbocharged engines work, their benefits and drawbacks, plus essential maintenance tips for optimal vehicle performance and longevity. So what is a turbocharger? In order to achieve this boost, the turbocharger uses the exhaust flow from the engine to spin a turbine, which in turn spins an air pump. While a turbocharger uses exhaust gases to propel the turbine that forces more air into the engine, a supercharger uses the motor’s belt system to turn a turbine that forces more. It enhances the performance and efficiency of ic engines by harnessing exhaust gases to compress. In order to achieve this boost, the turbocharger uses the exhaust flow from the engine to spin a turbine, which in turn spins an air pump. A turbocharger allows smaller engines to develop the power of a larger naturally aspirated engine. This extra fuel is where. This increase in air means. It does this without sacrificing fuel economy under conservative driving. When air is compressed the oxygen molecules are packed closer together. So what is a turbocharger? In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. A turbocharger, often called a turbo, is an integral component in modern ic engines. So what is a turbocharger? It is the job of the turbocharger to compress more air flowing into the engine’s cylinder. When air is compressed the oxygen molecules are packed closer together. The turbine in the turbocharger. A turbocharger allows smaller engines to develop the power of a larger naturally aspirated engine. This increase in air means. With a turbocharger, we harness some of the energy in the exhaust to drive the compressor, which allows the engine to burn more fuel each second. This extra fuel is where. In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by. It uses this energy to. While a turbocharger uses exhaust gases to propel the turbine that forces more air into the engine, a supercharger uses the motor’s belt system to turn a turbine that forces more. In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by. Learn how turbocharged engines work, their benefits and drawbacks, plus essential maintenance tips for optimal vehicle performance and longevity. So what is a turbocharger? It enhances the performance and efficiency of ic engines by harnessing exhaust gases to compress. In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that. So what is a turbocharger? In order to achieve this boost, the turbocharger uses the exhaust flow from the engine to spin a turbine, which in turn spins an air pump. A turbocharger, often called a turbo, is an integral component in modern ic engines. With a turbocharger, we harness some of the energy in the exhaust to drive the. It enhances the performance and efficiency of ic engines by harnessing exhaust gases to compress. It does this without sacrificing fuel economy under conservative driving. In order to achieve this boost, the turbocharger uses the exhaust flow from the engine to spin a turbine, which in turn spins an air pump. Learn how turbocharged engines work, their benefits and drawbacks,. It is the job of the turbocharger to compress more air flowing into the engine’s cylinder. It enhances the performance and efficiency of ic engines by harnessing exhaust gases to compress. When air is compressed the oxygen molecules are packed closer together. A turbocharger allows smaller engines to develop the power of a larger naturally aspirated engine. In order to. A turbocharger allows smaller engines to develop the power of a larger naturally aspirated engine. This extra fuel is where. It is the job of the turbocharger to compress more air flowing into the engine’s cylinder. It uses this energy to. Learn how turbocharged engines work, their benefits and drawbacks, plus essential maintenance tips for optimal vehicle performance and longevity. In order to achieve this boost, the turbocharger uses the exhaust flow from the engine to spin a turbine, which in turn spins an air pump. A turbocharger allows smaller engines to develop the power of a larger naturally aspirated engine. It does this without sacrificing fuel economy under conservative driving. In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known. In order to achieve this boost, the turbocharger uses the exhaust flow from the engine to spin a turbine, which in turn spins an air pump. A turbocharger, often called a turbo, is an integral component in modern ic engines. In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device. With a turbocharger, we harness some of the energy in the exhaust to drive the compressor, which allows the engine to burn more fuel each second. So what is a turbocharger? It enhances the performance and efficiency of ic engines by harnessing exhaust gases to compress. A turbocharger allows smaller engines to develop the power of a larger naturally aspirated engine. Learn how turbocharged engines work, their benefits and drawbacks, plus essential maintenance tips for optimal vehicle performance and longevity. While a turbocharger uses exhaust gases to propel the turbine that forces more air into the engine, a supercharger uses the motor’s belt system to turn a turbine that forces more. In order to achieve this boost, the turbocharger uses the exhaust flow from the engine to spin a turbine, which in turn spins an air pump. It uses this energy to. This extra fuel is where. This increase in air means. It does this without sacrificing fuel economy under conservative driving. In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (also known as a turbo or a turbosupercharger) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases.Turbo Size Chart Ponasa
Turbo and Supercharger Maps
Let’s Talk Turbochargers A Glossary of Common Turbo Parts & Components
Turbo and Supercharger Maps
Garrett Turbo Sizes Explained at Kristen Kerri blog
Turbo Dimensions Explained at Concepcion Pedigo blog
Turbo Size Calculator How It Works YouTube
The Warner S300 SXE An Inside Look AGP Turbochargers, Inc. Store
ATP TURBO The Premiere Provider of Turbocharging Components
Turbo Size
It Is The Job Of The Turbocharger To Compress More Air Flowing Into The Engine’s Cylinder.
The Turbine In The Turbocharger.
When Air Is Compressed The Oxygen Molecules Are Packed Closer Together.
A Turbocharger, Often Called A Turbo, Is An Integral Component In Modern Ic Engines.
Related Post: