Valence Electrons Periodic Table Chart
Valence Electrons Periodic Table Chart - The meaning of valence is the degree of combining power of an element as shown by the number of atomic weights of a monovalent element (such as hydrogen) with which the atomic. Capital of the drome department, valence is a sleepy city overlooking the rhone river. This capacity is called valence, and it varies periodically with increasing atomic weight. In methane, carbon has a valence of 4; An hour from lyon and grenoble and in close proximity to vineyards producing crozes hermitages, st. In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron associated with an atom that can form a chemical bond and participate in a chemical reactions. Introduced in 1868, the term is used to express. Look up valence, valence, valencies, or valency in wiktionary, the free dictionary. Valence, in chemistry, the property of an element that determines the number of other atoms with which an atom of the element can combine. Valence or valency may refer to: Valence or valency may refer to: The valence is the combining capacity of an atom of a given element, determined by the number of hydrogen atoms that it combines with. The noble gases all have valences of 0 because they almost never combine with any other element. Look up valence, valence, valencies, or valency in wiktionary, the free dictionary. An hour from lyon and grenoble and in close proximity to vineyards producing crozes hermitages, st. This is determined based on the number of electrons that would be added, lost, or. Valence, in chemistry, the property of an element that determines the number of other atoms with which an atom of the element can combine. This capacity is called valence, and it varies periodically with increasing atomic weight. Introduced in 1868, the term is used to express. Capital of the drome department, valence is a sleepy city overlooking the rhone river. The valence is the combining capacity of an atom of a given element, determined by the number of hydrogen atoms that it combines with. The noble gases all have valences of 0 because they almost never combine with any other element. Valence or valency may refer to: The meaning of valence is the degree of combining power of an element. The meaning of valence is the degree of combining power of an element as shown by the number of atomic weights of a monovalent element (such as hydrogen) with which the atomic. In methane, carbon has a valence of 4; This is determined based on the number of electrons that would be added, lost, or. An hour from lyon and. An hour from lyon and grenoble and in close proximity to vineyards producing crozes hermitages, st. In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron associated with an atom that can form a chemical bond and participate in a chemical reactions. In methane, carbon has a valence of 4; In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valency number,. The ability of an atom to combine with other atoms, measured by the number of electrons it will…. This is determined based on the number of electrons that would be added, lost, or. Valence or valency may refer to: Introduced in 1868, the term is used to express. Capital of the drome department, valence is a sleepy city overlooking the. Capital of the drome department, valence is a sleepy city overlooking the rhone river. The ability of an atom to combine with other atoms, measured by the number of electrons it will…. In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valency number, is a measure of the number of chemical bonds formed by the atoms of a given element. This. An hour from lyon and grenoble and in close proximity to vineyards producing crozes hermitages, st. The noble gases all have valences of 0 because they almost never combine with any other element. Valence or valency may refer to: Look up valence, valence, valencies, or valency in wiktionary, the free dictionary. The ability of an atom to combine with other. The valence is the combining capacity of an atom of a given element, determined by the number of hydrogen atoms that it combines with. In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron associated with an atom that can form a chemical bond and participate in a chemical reactions. Valence describes how easily an atom or radical can combine. The ability of an atom to combine with other atoms, measured by the number of electrons it will…. The valence is the combining capacity of an atom of a given element, determined by the number of hydrogen atoms that it combines with. Introduced in 1868, the term is used to express. In methane, carbon has a valence of 4; The. In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valency number, is a measure of the number of chemical bonds formed by the atoms of a given element. The meaning of valence is the degree of combining power of an element as shown by the number of atomic weights of a monovalent element (such as hydrogen) with which the atomic. The. Valence, in chemistry, the property of an element that determines the number of other atoms with which an atom of the element can combine. This capacity is called valence, and it varies periodically with increasing atomic weight. This is determined based on the number of electrons that would be added, lost, or. The ability of an atom to combine with. This is determined based on the number of electrons that would be added, lost, or. The ability of an atom to combine with other atoms, measured by the number of electrons it will…. In methane, carbon has a valence of 4; An hour from lyon and grenoble and in close proximity to vineyards producing crozes hermitages, st. Valence, in chemistry, the property of an element that determines the number of other atoms with which an atom of the element can combine. Look up valence, valence, valencies, or valency in wiktionary, the free dictionary. Valence describes how easily an atom or radical can combine with other chemical species. This capacity is called valence, and it varies periodically with increasing atomic weight. Valence or valency may refer to: In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valency number, is a measure of the number of chemical bonds formed by the atoms of a given element. In chemistry and physics, a valence electron is an electron associated with an atom that can form a chemical bond and participate in a chemical reactions. Introduced in 1868, the term is used to express.Periodic Table Valence Electrons Chart Ponasa
Valence Electrons Chart Teaching chemistry, Chemistry classroom, Periodic table
Periodic Table Valence Electrons Chart Ponasa
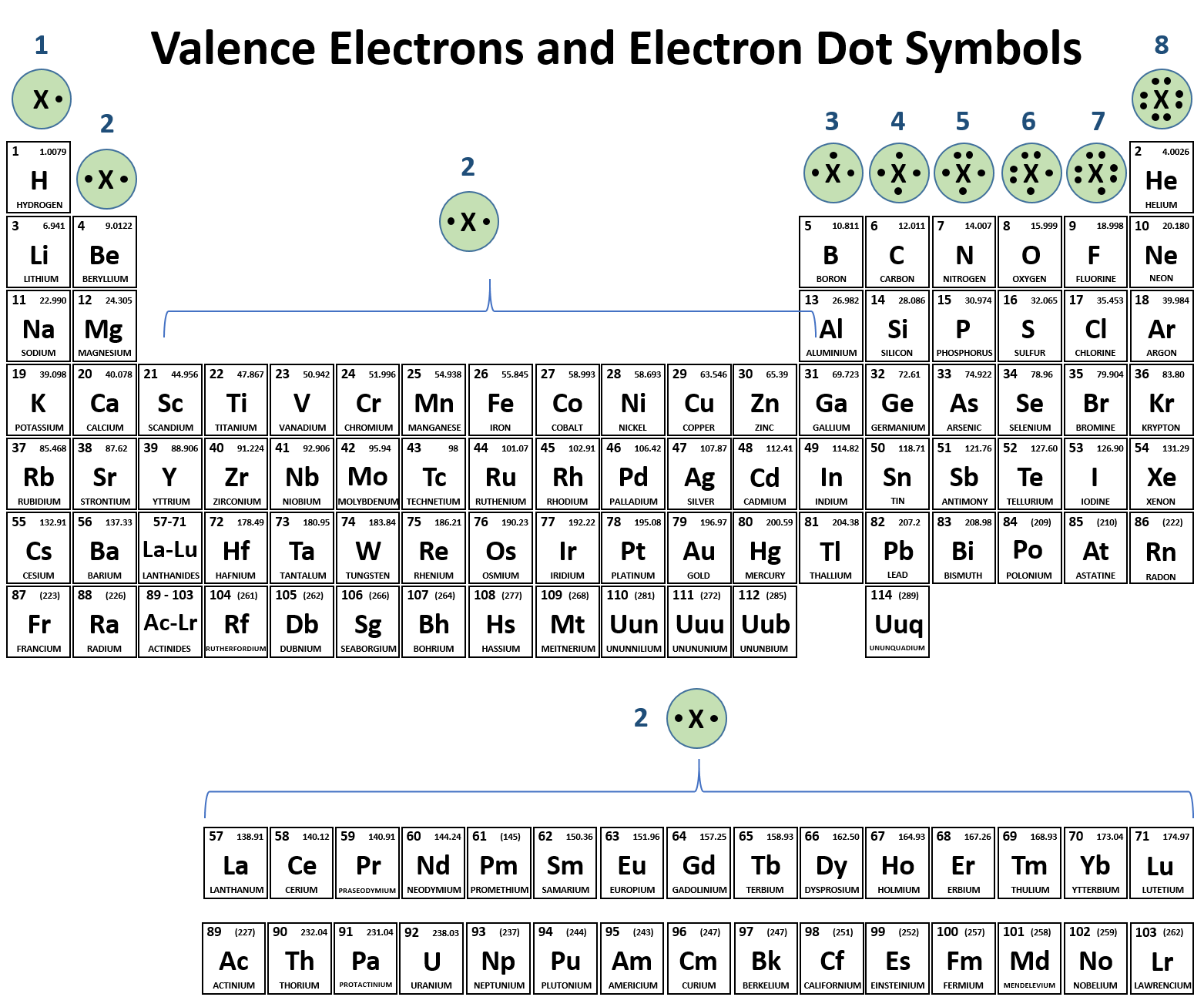
Valence Electrons Chart of Elements (With Periodic table)
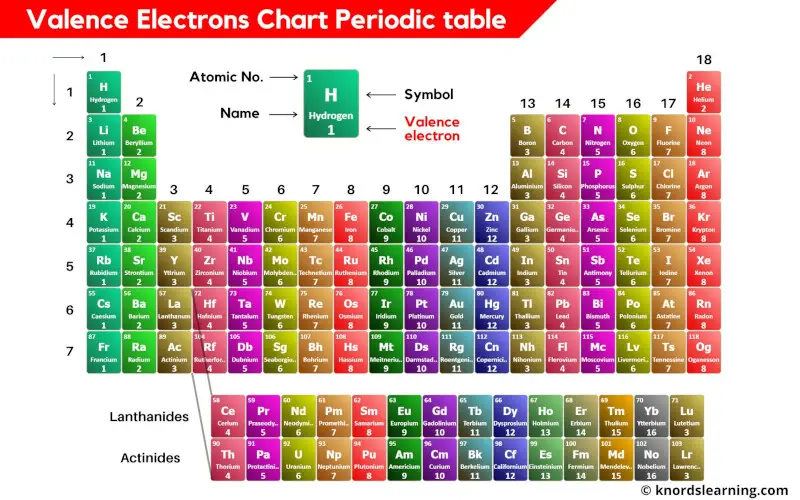
Free Printable Periodic Table (With names, charges & Valence Electrons) [PDF] Printables Hub
Valence Electron Chart Periodic Table 2024 Periodic Table Printable
Free Printable Periodic Table (With names, charges & Valence Electrons) [PDF] Printables Hub
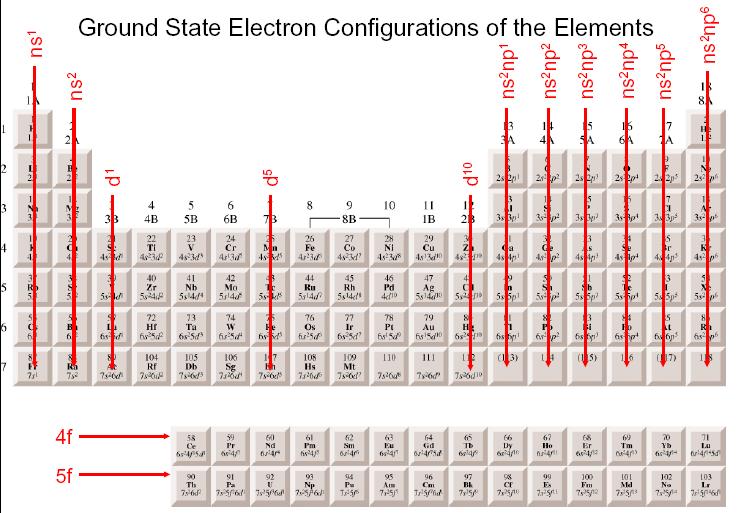
What Are Valence Electrons? Definition and Periodic Table
Valency of Elements Valencies of 118 Periodic Table Elements
Valence Electrons Periodic Table Chart 3 1 Periodic Table Mun Ib Images
Capital Of The Drome Department, Valence Is A Sleepy City Overlooking The Rhone River.
The Valence Is The Combining Capacity Of An Atom Of A Given Element, Determined By The Number Of Hydrogen Atoms That It Combines With.
The Noble Gases All Have Valences Of 0 Because They Almost Never Combine With Any Other Element.
The Meaning Of Valence Is The Degree Of Combining Power Of An Element As Shown By The Number Of Atomic Weights Of A Monovalent Element (Such As Hydrogen) With Which The Atomic.
Related Post:

![Free Printable Periodic Table (With names, charges & Valence Electrons) [PDF] Printables Hub](https://printableshub.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/periodic-table-04-2048x1457.jpg)

![Free Printable Periodic Table (With names, charges & Valence Electrons) [PDF] Printables Hub](https://printableshub.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/periodic-table-01-2048x1457.jpg)


